A Comprehensive Guide to Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is increasingly popping up in conversations and articles. But, like so many things, references to it may sometimes need to be better understood. In short, Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to a significant transformation in how industries operate. It represents a major paradigm shift in manufacturing and production processes. It is driven by blending advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, cloud computing, and additive manufacturing (3D printing). But before getting into the details of Industry 4.0, let’s begin with a real example of how its application to a well-recognized company transformed its production and operations.
Industry 4.0 in Play
Heineken is recognized as a global brewing titan established in 1864. It is currently ranked as the world's second-largest brewer, owning over 160 breweries across more than 70 nations and selling upwards of 8.5 million barrels from its diverse portfolio of beers within the United States alone. Despite its success, the company recognized it still had room for improvement.
Using data-driven advancements with artificial intelligence augmentation, it was discovered that the company had a significant production bottleneck at its Mexican plant, obstructing the production of several million cases of beer. It was also revealed that a production bottleneck occurred during the filtration stage as beer transitioned from maturation and filtration into bright beer tanks (BBTs). Facility-wide disturbances and demand-based production modifications led to unanticipated delays in the latter stages of production and product delivery. Making matters worse, the rescheduling process involved checking handwritten logs before manually inputting information into locally stored spreadsheets, which was costly and time-consuming.
Recognizing the value of these findings, Miguel Aguilera (Supply Chain Digital Transformation and Innovation Manager at Heineken Mexico) spearheaded a full implementation after participating in a brief course at MIT Sloan on Industry 4.0's impact on manufacturing operations. He then started the implementation by integrating enterprise resource planning alongside in-floor sensors for digitizing brewery processes. Once in place, machine learning techniques were employed via real-time data for optimizing filtering procedures and daily BBT schedules. The results were reductions in BBT utilization and filtration times per cycle. These improvements led to marked monthly enhancements relating to overall brewing capacity and returns on investment. Results were evident within one-month post-implementation.
This digital transformation led the Heineken Mexico facility to create an unobstructed view of bottling lines and receive read-outs on filtration conditions for each batch made. Moreover, AI continuously monitors production, automatically refining efficiency at every juncture and allowing factory personnel to make adjustments without impeding the manufacturing process. Because of the Industry 4.0-inspired operations modifications,, operators now possess the ability to perform their duties effectively—even from remote locations.
Now, let’s move on to exploring where Industry 4.0 got its beginnings, its technologies and challenges, and more.
Industry 4.0 and its Predecessors
The term ‘Industry 4.0’ is relatively new, with the first mention of it in 2016 by the founder and executive chairman of the World Economic Forum, Professor Klaus Schwab. As noted previously. Industry 4.0 refers to the ongoing transformation in manufacturing driven by disruptive trends such as data proliferation and connectivity, advanced analytics, human-machine collaboration, robotics enhancement, augmented reality integration, and machine automation. Industry 4.0 is a digital transformation of traditional business models, processes, and operations.
Looking back, the 21st-century digital revolution has ushered in an era characterized by increased connectivity, sophisticated analytics capabilities, enhanced automation technologies, and cutting-edge manufacturing advancements that have been reshaping global businesses for years. This shift commenced in the middle of the last decade, with substantial potential to impact operations and future production models.
Historically, the genesis of each industrial revolution goes back to a primary innovation. For example, steam power drove the first iteration. Next, electricity fueled its successor, followed by preliminary automated machinery engineering underpinning the next stage. The fourth industrial revolution, Industry 4.0 is being aided and is continuously accelerating because of the explosion in intelligent computing. Intelligent computers or cyber-physical systems that characterize Industry 4.0 have been built on top of the digitization that marked the third industrial revolution. And so it goes!
Industry 4.0 integrates
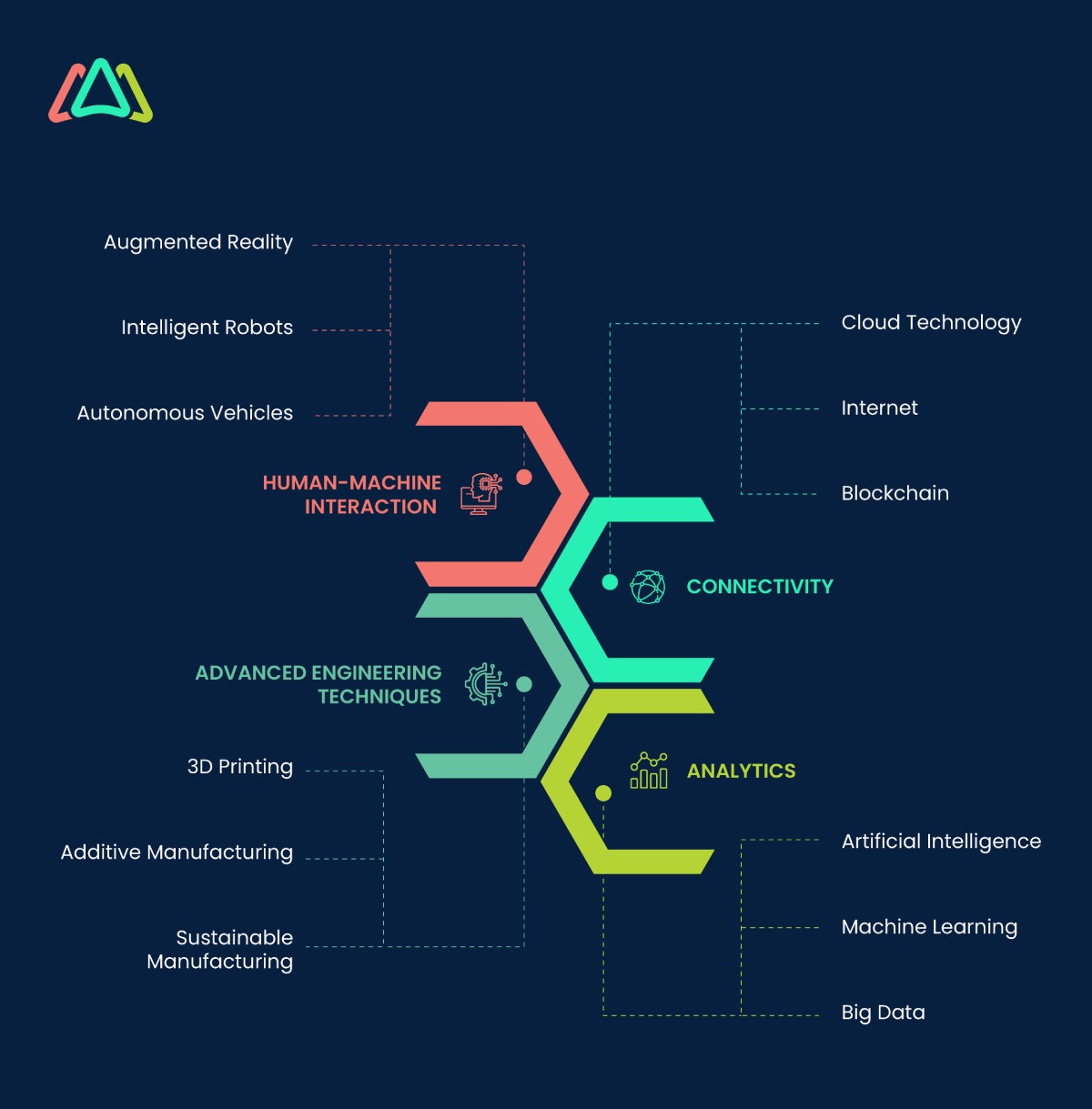
McKinsey summarizes the scope of Industry 4.0 by highlighting how it addresses integrating four foundational disruptive technologies across value chains. The technologies are:
(1) Connectivity via cloud technology encompassing internet accessibility enabled through blockchain applications alongside sensor deployment.
(2) Analytics incorporating advanced methodologies utilizing artificial intelligence-driven strategies.
(3) Human-machine interaction manifested in virtual reality environments supplemented with autonomous vehicles employing robotics-based mechanisms.
(4) Advanced engineering techniques exemplified by additive manufacturing processes like three-dimensional printing innovations coupled with renewable energy sources exploiting nanoparticles' properties.
Importantly, technology constitutes only half of this industrial equation. Companies must prioritize employee development initiatives comprising upskilling efforts, equipping workers with novel proficiencies relevant to evolving roles, and reskilling endeavors to retrain employees for alternate organizational positions when necessary. This can deliver sustainable advantages to companies over an extended period.
Industry 4.0 Benefits
Advantages for businesses that proactively adopt Industry 4.0 principles include greater accessibility to products/services while rendering them easily transmissible for consumers and stakeholders along the value chain. Successful implementation of 4IR technologies can result in more efficient supply chains, increased productivity levels during working hours, reduced waste generation within factories, and myriad other benefits accrued by employees, stakeholders, and end-users alike.
- Increased efficiency - By leveraging technologies like robotics and AI, companies can automate mundane processes and free up employees’ time to focus on more complex tasks.
- Improved customer experience – Automation allows companies to process requests quickly and accurately, providing customers with a seamless experience.
- Improved cost savings – Automating processes can help reduce costs associated with manual labor, safety, and operational efficiency.
Here are two industry examples to illustrate the above:
DHL is an international logistics company leveraging Industry 4.0 technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The company has developed an IoT network to track goods in real-time and uses predictive analytics to anticipate customer demand and identify potential delays. They have also implemented automated warehouses (including automated guided vehicles) and robotic sorting systems to speed up sorting packages.
Mercedes Benz is a global leader in automotive technology and has adopted Industry 4.0 technologies to create better products for their customers. The company has developed an AI-powered virtual assistant that helps drivers navigate and personalize their vehicles and a cloud platform to share data across different departments. They have also used 3D printing to produce parts faster and reduce costs.
Industry 4.0 is already changing the way we do business. Companies can quickly respond to market trends and capitalize on new opportunities before their competitors. The growth statistics on Industry 4.0 are also trending.
Growth Statistics
In 2022, IoT Analytics, a leading global provider of market insights and strategic business intelligence on IoT, AI, Cloud, Edge, and Industry 4.0, put together an interesting blog post on Industry 4.0 growth statistics. The blog highlights the growth in Industry 4.0 from 2011 as follows:
- Industry 4.0 Adoption - In the 2022 Industry 4.0 adoption survey, 72% of the respondents report implementing Industry 4.0 with many initiatives in progress and some already completed. In 2015, over 88% needed to learn what Industry 4.0 was.
- Funding Opportunities - Increasing start-up funding and M&A deals is another metric to consider for the growth trend. The annual funding of Industry 4.0 start-ups has increased by 319% from 2011 to 2021. The yearly number of Industry 4.0-related M&A deals has increased 116% in the past 10 years.
- Publishing - Over 200,000 Industry 4.0 academic papers have been published within 10 years. It points to increasing interest in the subject. The increase in searches on Google also corroborates this growing interest. Searches for Industry 4.0 on Google in 2022 are 140 times higher compared to the year it was first introduced and made public (2011). Also, related terms such as Industrial IoT and Smart Manufacturing have grown 32 times.
Impact of Industry 4.0
The impact of Industry 4.0 is far-reaching. Its effect touches all aspects of business, as well as societal impact. It is revolutionizing industries by enhancing productivity, reducing operational costs, and enabling greater customization in manufacturing. Furthermore, Industry 4.0 is reshaping the job landscape, emphasizing digital skills and shifting towards more collaborative human-machine work environments. Additionally, it can drive sustainability efforts, as smart technologies can lead to more efficient resource utilization.
Impact on the Economy
McKinsey projects Industry 4.0’s value creation potential for manufacturers and suppliers to reach $3.7 trillion by 2025. McKinsey's research points out that Industry 4.0 front-runners, facilities well on their way to adopting AI and other advanced technologies by 2025 can expect a 122 percent positive cash flow change. Follower companies can expect just 10 percent, while companies that wholly fail to adopt AI could see a 23 percent downturn.
On Business Models
As the impact of Industry 4.0 reverberates across various sectors, business models have experienced a significant shift toward customer-centricity over product-centricity. Companies now harness data analytics to gain insights into consumer needs and fine-tune their offerings accordingly. This has allowed companies to differentiate from competitors and increase revenues.
No longer solely manufacturing entities, these organizations must adopt the mindset of a “Data Company” to differentiate themselves from competitors and enhance profitability. Consider Tesla. Is it merely an automaker or a “Data Company” that continuously delivers value to its customers by learning from them? Reflecting upon this question can inform our perspective on Industry 4.0.
Impact on Society
Societal ramifications constitute another aspect influenced by Industry 4.0's technological advancements. It has created a paradoxical situation. Automation has increased unemployment rates while simultaneously intensifying the demand for upskilling and reskilling efforts among workers who struggle to adapt due to age or other limitations. How shall society address individuals unable or unwilling to embrace the changes wrought by Industry 4.0?
McKinsey foresees the following changes in the coming decade.
- Demand for physical and manual skills in repeatable tasks, like those on assembly lines, will decline by nearly 30 percent.
- Demand for basic literacy and numeracy skills will decline by almost 20 percent.
- Demand for technological skills such as coding will rise by more than 50 percent.
Impact on Supply Chain
Last, supply chains have undergone considerable transformations under this new industrial paradigm as well—real-time tracking technologies paired with predictive analytics facilitate more efficient operations by reducing delays and stock shortages. Digitalization fosters greater transparency within supply chain networks by granting businesses comprehensive visibility into suppliers' and customers' activities. Moreover, advanced analytical capabilities enable the detection of patterns previously imperceptible through human observation alone.
By comprehensively monitoring supply chains from inception through completion using innovative tools borne out of Industry 4.0 developments, global communities may better preempt future disruptions similar to those witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic era.
The potential impact of Industry 4.0 will require tremendous effort on the part of the stakeholders. Implementation teams will have to be prepared for a long list of challenges.
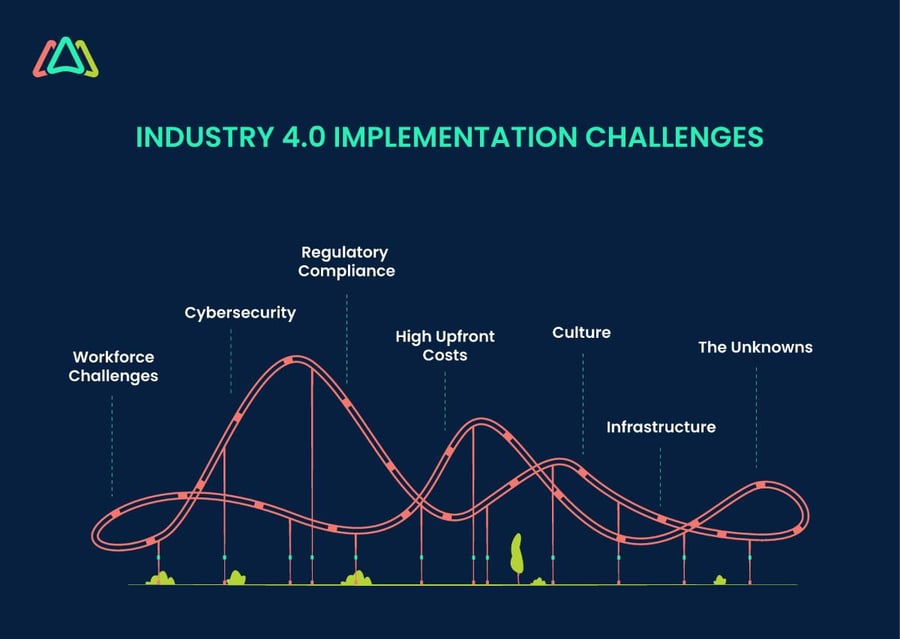
Implementation Challenges
Let’s turn to the areas where implementation teams are expected to face challenges. The challenges noted will depend on the situation of the company implementing Industry 4.0 solutions.
Workforce Challenges
Industry 4.0’s most profound impact would be on the workforce. How the workforce is managed, supported, and aligned will determine companies' eventual success with Industry 4.0. Unemployment and skilling are the two most important factors.
Loss of jobs:
Unemployment and the fear of job loss have remained a constant concern since steam propelled the first industrial revolution. Since then, this factor has only compounded. This is also true for Industry 4.0. While it can potentially reduce or eliminate specific job roles, leading to a need for retraining and upskilling workers, will the inherent risk of unemployment be manageable considering its impact? Organizations must consider this from the ethics, sensitivity, and pragmatism angle.
Skilling
Companies know the potential skill gap that can arise from automating specific tasks. The emergence of Industry 4.0 has led to an increased demand for skilled workers who can work with digital technologies. Organizations must invest in training and development programs to prepare their workforce for the future. But, companies would be committing a grave mistake if they looked at this as just a training and development intervention. The skill challenge is much greater than this because it is a human capital challenge. Companies must look at skilling strategically and create different roadmaps for upskilling, reskilling, and staffing. Upskilling is learning new skills to do better in the current roles. Reskilling is the more significant challenge. Here, identified teams learn new skills to take on brand-new functions.
Cybersecurity
As Industry 4.0 technologies become more prevalent, companies must ensure their data is secure and protected from cyber threats. As more and more data is stored digitally, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Companies must invest in cybersecurity measures to protect their data and operations.
The widespread usage of the internet has normalized cyber crimes and online fraud. Companies and individuals are already aware of the need to manage the risk of cyber nuisance. Unfortunately, all this comes at an additional cost. But the investment is necessary because of the consequences. Here are some statistics.
- US $ 4.45 million - According to IBM, in 2023, the global average data breach cost was USD 4.45 million, a 15% increase over 3 years.
- US $ 10.5 trillion - Research from Cybersecurity Ventures expects global cybercrime costs to grow by 15 percent per year over the next five years, reaching USD 10.5 trillion annually by 2025, up from USD 3 trillion in 2015. This USD 10.5 trillion number is staggering since it exceeds the GDP of all countries except the top 2.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance presents a formidable obstacle in Industry 4.0 implementations for various reasons, including the significant increase in data generation from humans and machines. As extensive data is produced, avoiding privacy breaches or leakage becomes vital. Consequently, addressing these concerns from a compliance standpoint is imperative.
Another challenge lies in determining accountability. Since Industry 4.0 relies heavily on automation and machine decision-making processes, pinpointing liability for any actions machines take is a grey area.
Moreover, existing legal frameworks and regulations have not kept pace with rapid advancements in Industry 4.0 technology. Many laws still pertain to earlier industrial eras (Industry 3.0 or 2.0). As issues are bound to arise, resolving them within the context of outdated legislation will be challenging.
Rectifying this situation requires concerted efforts from compliance teams within businesses involved in Industry 4.0 and industry forums that promote stakeholder cooperation regarding adherence requirements and uniform standards.
High Upfront Costs
High initial costs present another hurdle surrounding implementation. Companies must be prepared to invest substantially into hardware and software solutions that facilitate digital transformation initiatives—an expensive prospect. Businesses should consider potential return-on-investment figures as part of the feasibility studies because Industry 4.0 solutions will eventually lead towards long-term benefits in costs and productivity, much above the initial upfront investment.
A recommended approach is gradual investment stages rather than committing all resources simultaneously. With this stepwise approach, organizations will better manage financial outlays over time.
Culture
All organizational transformation projects require leadership commitment and drive. The same applies to Industry 4.0 projects. All Industry 4.0 success stories have stressed the importance of leadership. Although the focus of implementing Industry 4.0 is on organizational change, company heads must also consider changes to the organization’s culture.
Bureaucracy and an existing legacy culture could scuttle such initiatives. Industry 4.0 calls for organizations to actively catalyze organizational culture to be prepared to implement Industry 4.0 successfully. The management consulting firm EY says an organization’s culture comprises three parts: mindset, behavior, and skill. Understanding this can help teams strategically shift culture through practical behavior changes. These factors are vital to creating an agile and sustainable way to catalyze Industry 4.0 transformation. EY also points out that senior leadership should ruthlessly focus on removing roadblocks and enhance all attempts to inhibit a smooth culture change.
Infrastructure
Numerous obstacles exist when implementing Industry 4.0 solutions due to infrastructural conditions. Companies considering investing in this domain must evaluate whether they possess the requisite network, storage, and computing capabilities to support these advanced technologies.
It is crucial to assess continuously evolving private infrastructure and examine public infrastructure that ensures sustainable development of certain Industry 4.0 solutions. An example lies in the availability of a 5G network, an essential component for facilitating machine-to-machine and human-machine interactions at opportune moments. Moreover, sufficient electricity supply remains a vital entity. Electric vehicle demand illustrates how increased pressure strains legacy power grids unequipped for such requirements.
Transitioning from legacy systems presents another challenge. Manufacturing organizations seeking integration with Industry 4.0 will face significant changes concerning skills acquisition while simultaneously writing off investments and capitalizing costs.
The Unknowns
Beyond the above challenges are other impediments to unknowns within Industry 4.0's implementation process. Unforeseen difficulties may emerge as companies adopt new technologies associated with this paradigm shift.
For instance, consider Google's Chatbot Lambda controversy involving software engineers debating its potential sentience. This prime example illustrates unforeseeable complications arising from cutting-edge technology adoption.
The challenges of implementing Industry 4.0 are multifaceted and require addressing regulatory compliance, investment considerations, and organizational cultural shifts. Businesses may successfully navigate this complex landscape by recognizing these obstacles and strategizing effective solutions tailored to each unique situation. Understanding the technologies driving Industry 4.0 will help make the ride easy.
Key Technologies Driving Industry 4.0
At the core of Industry 4.0 are several groundbreaking technologies reshaping industries and how we work. This section will explore the critical technologies driving Industry 4.0 and how they revolutionize the landscape.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things is the backbone of Industry 4.0. It involves connecting people, everyday systems, and machines to the internet, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In manufacturing, sensors and devices are embedded in machinery, products, and even the factory environment. This connectivity provides real-time insights into the status and performance of assets, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and improved decision-making. IoT is the foundation upon which the future smart factory will be built. OIT isn’t about the hardware. It’s primarily about data. Industry 4.0 adopters would do well to think of IoT sensors beyond hardware because there’s a tendency to overlook its primary purpose of capturing data by sensors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are powering automation and intelligence across various industries. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions, while AI systems can learn and adapt to new situations. In Industry 4.0, AI is applied to quality control, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization tasks. These technologies enhance efficiency and enable businesses to make data-driven decisions, improving overall performance. There is a risk of thinking of AI and ML just as analytics. It does not stop at that. Every analytics step adds to the body of existing intelligence. And this intelligence is tapped into to solve the following problem. A case in point is when the IBM Deep Blue supercomputer defeated Gary Kasparov in chess.
Big Data and Analytics
The data generated by IoT devices and other sources in Industry 4.0 is massive and complex. Large datasets are collected from IoT sensors in factories, warehouses, and other industrial sites. Big data analytics involves processing and analyzing this data to extract valuable insights. By leveraging advanced analytics tools, businesses can identify trends, detect anomalies, and make more informed decisions. Big data analytics is especially valuable in optimizing production processes, demand forecasting, and enhancing the customer experience through personalized products and services.
Cyber-Physical Systems
Also referred to as intelligent computers, cyber-physical systems (CPS) represent digital and physical systems integration. These systems bridge the gap between the virtual world of data and the physical world of machinery and equipment. The smartphone we commonly use is a fine example of a CPS. In manufacturing, CPS can enable real-time adjustments to production based on data analytics, ensuring optimal quality and efficiency. They also facilitate the seamless interaction between humans and machines, enhancing collaboration and productivity. Augmented reality, autonomous robots, and additive manufacturing are further examples of cyber-physical systems, some of which will be used in future factories.
A Peek into the Factories of the Future
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are propelling the factories of the future toward a new paradigm. Envision a self-organizing factory that autonomously adapts to shifting requirements, fostering seamless collaboration between humans and machines.
The manufacturing process commences in virtual reality, employing simulation technologies. The cyber-physical production system initially assesses the feasibility of production. Subsequently, machines within the facility furnish comprehensive data regarding their capabilities and limitations.
Utilizing this information, the system creates a digital twin of the product and juxtaposes requisite production steps with available skills possessed by humans and machinery in the factory. Each machine derives knowledge of specific manufacturing procedures directly from its digital counterpart.
Informed by assembly specifications for parts, all necessary actions are dynamically calculated. enabling autonomous execution of production processes steered solely by each product itself. This is an embodiment of Industry 4.0 principles.
Through machine learning algorithms coupled with intelligent sensors and speech recognition technology, these advanced systems continually refine their abilities while optimizing efficiency within existing workflows and enhancing product quality output.
Safety protocols are meticulously devised to guarantee harmonious coexistence between people and machinery during collaborative endeavors. Cyber-physical production systems will better serve consumer demands by expediting precise customization while improving operational efficacy throughout industrial fabrication processes.
These key technologies are interwoven, working to drive Industry 4.0 forward. Their collective impact transforms traditional industries into highly efficient, adaptive, and data-driven ecosystems. Soon, embracing these technologies will no longer be a choice. Instead, they’ll be necessary for businesses wanting to remain competitive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
US Manufacturing - Back to the Future with Industry 4.0?
US manufacturing is getting ready to make a comeback. According to McKinsey research, an effective transformation of the US manufacturing sector could boost the GDP by $275 billion to $460 billion while adding up to 1.5 million jobs. These projections are encouraging since the number of manufacturing plants in the United States has fallen roughly 25 percent since 1997.
Manufacturers will need to embrace Industry 4.0 technologies to stay relevant and competitive. With the help of these technologies, they will be able to increase production efficiency while reducing costs. Digital twins, IOT-enabled predictive maintenance, robotics, and automation will enable faster response times and higher-quality output. Industry 4.0 will play a critical role in the US manufacturing renaissance.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





