
How Industry 4.0 is Reshaping the Landscape of US Manufacturing
US manufacturing is making a coming back. McKinsey's research reported that, by effectively transforming (digital transformation) the US manufacturing sector, it could boost the GDP by $275 billion to $460 billion while adding up to 1.5 million jobs. These projections are encouraging since the number of manufacturing plants in the United States has fallen roughly 25 percent since 1997.
Industry 4.0 refers to companies integrating new technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, and AI and machine learning into their production facilities and operations. Changing the way manufacturing companies run their operations is responsible, in part, for galvanizing the growth within its industry sector. With the help of these technologies, manufacturers can capture opportunities and increase production efficiency while reducing costs simultaneously. More specifically, Industry 4.0 technologies such as digital twins, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance, robotics, and automation enable faster response times, higher-quality output, and reduced downtime. Because of these capabilities, Industry 4.0 is staged to play a critical role in the US manufacturing renaissance.
Every year, Deloitte surveys 100 US executives across the manufacturing sector to understand their outlook, perspectives, and challenges. The survey captures insights from nine specific industry segments, spanning electric equipment to specialty materials manufacturing. The 2023 survey identified five trends, three directly influenced by Industry 4.0. The three trends related to Industry 4.0 were; 1) a continuous investment in Industry 4.0, 2) leveraging new technologies to improve supply chain issues, and 3) moving toward smart manufacturing. Based on the strong involvement of Industry 4.0 factors, Deloitte deemed it a megatrend.
1. Continuous Investment in Digital Technologies
The COVID-19 pandemic presented essential lessons to us all, and as a result, most businesses altered their strategies in response to it. Companies with the foresight to invest in digital technologies emerged from the chaos stronger and more resilient. Those forward-thinking businesses pivoted more confidently than businesses that needed to be faster to implement digital strategies. Similarly, firms with higher digital implementation possessed clearer supply chain visibility, adapting quickly to the numerous challenges that COVID-19 presented.
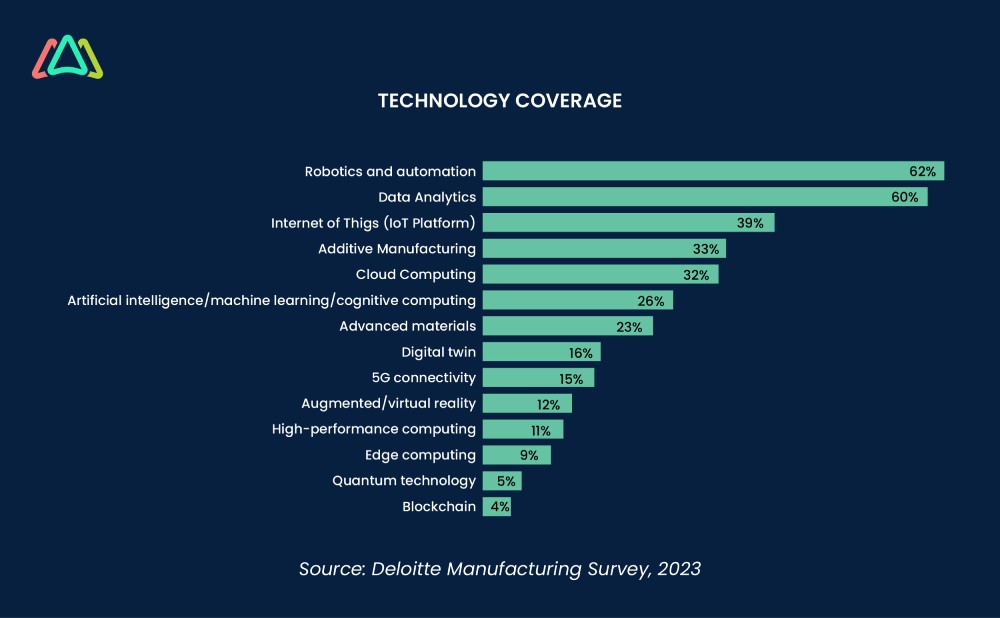
The illustration above highlights the range of Industry 4.0 technologies survey participants plan to focus on to increase operational efficiency and strengthening their core around automation, data analytics, and IoT. Advanced interventions like blockchain, quantum tech, and edge computing were indicated, but to a lesser degree.
Continued investments in advanced manufacturing technologies could be the key to unlocking the agility needed in uncertain times. Inflation has been a factor in the U.S. economy, with the Federal Reserve carefully steering the economy. With a look toward the next 12-18 months, manufacturers' digital strategies will likely sway between tactical and strategic-driven approaches. On a tactical level, some facilities have accelerated warehouse automation to counter pandemic-induced labor shortages. A surge in automation may fuel productivity and transform the workforce composition within the industry. Strategically, companies’ focus on maintaining investment momentum enables them to pivot swiftly. Enhanced data and analytics capabilities can sharpen forecasting while accelerating value mapping of suppliers and raw materials. Furthermore, by utilizing advanced analysis strategies, preventive measures can be implemented during uncertain periods and ultimately bolster long-term profitability.
2. Supply Chain: Time-tested Mitigation Strategies Plus Digital Tech
Supply chain challenges emerged in the shadow of the pandemic. Deloitte's recent survey confirmed this, with 80% of manufacturing executives finding their supply chains heavily disrupted over the past year and a half. Furthermore, 72% of respondents foresee persistent shortages of critical materials and ongoing disruptions as the most significant uncertainty for the industry in the coming years.
It is not surprising that these executives are choosing to prioritize implementing Industry 4.0 digital technologies, which represents an effort to gain network visibility and respond to disruptions with unwavering confidence. As companies recalibrate their supply chain exposure, many turn to digital capabilities that illuminate their supply networks and enhance control and coordination.
Deloitte's Chief Procurement Officer (CPO) survey also revealed the technologies invested in, with advanced digital solutions at the forefront. It also reported that high-performing companies are more likely to have fully developed advanced analytics, visualization capabilities, RPA solutions, predictive analytics, and cognitive abilities. The most valuable digital capabilities implemented include diagnostic analytics, visualization, predictive technologies, RPA, and artificial intelligence.
Digital capabilities can help procurement organizations improve data visibility, collaborate effectively with suppliers, and enable greater agility within their organizations and across extended supply networks. Chief Product Officers (CPO) can harness the potential of the Internet of Things, 5G, blockchain, control towers, and AI-enabled collaborative workflows to elevate their digital prowess.
While not all interventions to mitigate supply chain risk rely on digital technologies, time-tested approaches endure. The challenge for suppliers is to navigate these risks through relationship management and supply chain collaboration with partners beyond tier-one suppliers, building redundancy via multiple suppliers, and boosting local capacity. This approach is a trend gaining traction in the US.
Integrating businesses across the value chain reduces exposure to logistics issues and transportation bottlenecks. In light of current disruptions, global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) have committed to opening new production facilities in US locations, bolstering local production capacity for parts and materials. Statutory enablers, such as incentives in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), the CHIPS Act, and the IRA, are expected to fuel this trend, increasing US manufacturing capacity and strengthening the supply chain's resilience against future storms.
3. Smart Manufacturing and Digital Transformation
Industry 4.0 is synonymous with smart manufacturing and smart factories. As smart factory transformation increases, manufacturers strive to secure their future competitiveness. Many invest in technological foundations, with trailblazers striving for connectivity through the cloud, edge computing, and 5G. As these digital cornerstones unfold, large-scale manufacturers integrate with partners across their value chain. Over 60% of surveyed executives join specialized technology firms, propelling their smart manufacturing ambitions into the coming years.
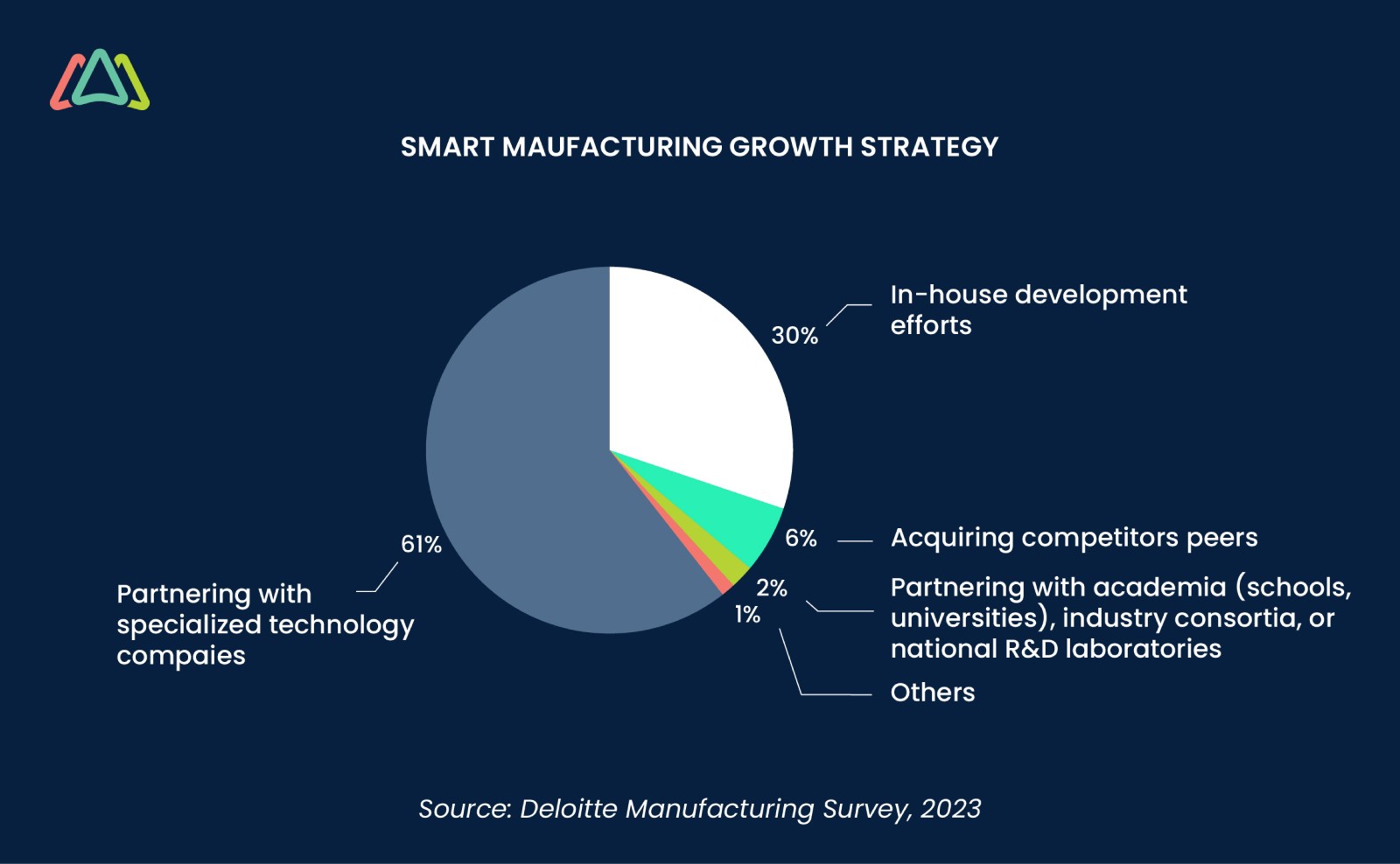
An example of an ecosystem approach is an electronics manufacturer collaborating with a research university and a telecommunications company. Together, they create a fully enabled private 5G production environment, testing use cases for industrial facilities.
With the digital core established, manufacturers delve into disruptive technologies such as augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), additive manufacturing, blockchain, and advanced analytics. A case in point is using augmented technologies alongside digital twins for employee training and reskilling. Another is the implementation of drones, cloud, and sensor technologies with augmented reality (AR) for quality control processes in the aerospace sector.
Early adopters experiment with digital technologies to interact and collaborate in a reality experience akin to a metaverse. The Deloitte survey reveals that one in five manufacturers is exploring underlying solutions or developing a metaverse platform for their products and services. A global automotive manufacturer explores the metaverse using a virtual factory simulating an actual production line while replicating the entire process digitally to ensure seamless operations before physical factory activation. Technicians in its service centers don AR glasses to complete intricate repairs in a virtual environment while connecting with other experts to work collaboratively on problems using digital twins.
As manufacturers consider the metaverse, cybersecurity issues will continue to be a concern.
Companies and individuals already know the need to manage the risk of cyber-related concerns, which come at an additional but much-needed cost.
Industry 4.0’s Indirect Impact
Industry 4.0 indirectly impacts talent management and corporate social responsibility.
The labor market is seeing an increase in job openings and record levels of new hires. Persistent workforce shortage, exacerbated by supply chain constraints, impacts the operational efficiency margins. In response, manufacturers develop strategies to retain talent, with upskilling and reskilling being prioritized.
With digital gains, the demand for advanced technical and digital skills also increases. Yet, skilled workers still need to be discovered. To bridge this gap, manufacturers are investing in continuous training initiatives, establishing partnerships with startups to tap into fresh talent and technology, and partnering with academic ecosystems to acquire digital expertise.
Corporate social responsibility focuses on reducing carbon emissions and attaining carbon neutrality. Technology-enabled smart buildings emerge as potential allies in this quest for sustainability. From optimizing machines and production lines to sensor-driven heating and cooling systems and energy-efficient lighting, these innovations pave the way for cost savings and a cleaner power supply. Of the surveyed manufacturing executives, 70% concurred that technologies bolstering energy efficiency could render their operations more sustainable. For example, one technology manufacturer has already achieved carbon neutrality for its corporate emissions by harnessing 100% renewable electricity.
A couple of questions remain. Can we expect too much from Industry 4.0? Will it deliver on its promises? Implementers are in the best place to answer, but time will tell. The very foundations of Industry 4.0 are subject to change as technological advancements continue to unfold. As such, keeping a watchful eye on this ever-evolving space is needed.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





