Embracing the Future with Prescriptive Maintenance
As a maintenance professional, I've witnessed the incredible transformation our industry has undergone in recent years. The advent of predictive maintenance has empowered us to anticipate equipment failures and prevent costly downtime, but there's a new frontier on the horizon - prescriptive maintenance. In this article, I'll delve into prescriptive maintenance, its benefits, and how cutting-edge software can drive the evolution of prescriptive maintenance.
What is Prescriptive Maintenance?
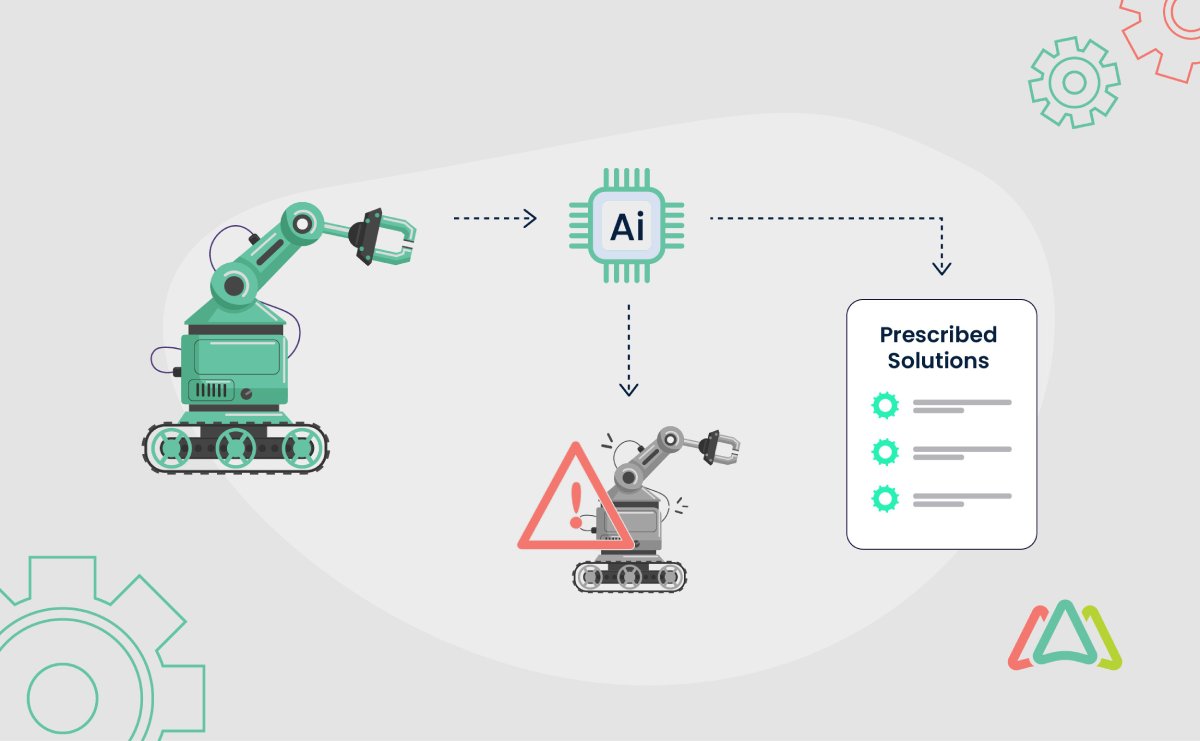
Prescriptive maintenance builds on predictive maintenance and is the next logical step. While predictive maintenance systems use historical data and sensor readings to forecast when equipment might fail, prescriptive maintenance goes further. It not only predicts failures but also prescribes specific actions to mitigate them, optimizing maintenance strategies and asset performance even more.
Prescriptive maintenance leverages sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to provide actionable recommendations, enabling maintenance teams to:
- Identify the root causes of potential failures.
- Suggest precise maintenance tasks.
- Optimize maintenance schedules based on resource availability.
- Minimize unnecessary maintenance to reduce costs.
Many industries have already seen the benefits of predictive maintenance (PdM). Prescriptive maintenance goes beyond PdM by using machine learning to improve an organization's operations. Unlike predictive maintenance, which focuses on simple decisions like whether to do maintenance or not, prescriptive maintenance offers a range of options and outcomes.
For instance, stopping production can be avoided by reducing compressor pressure or keeping machine speed low. This can delay downtime and help plan better for new equipment. It can also time out scheduled maintenance to meet a planned or urgent delivery order. Prescriptive maintenance can also spot future expenses before operators do, allowing better timing for purchases.
Predictive vs Prescriptive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses machine learning to schedule plant maintenance before equipment fails. It helps avoid sudden corrective actions. However, prescriptive maintenance (RxM) finds failure signs and advises on preventing or delaying them. It studies past data and creates possible scenarios. This way, costly and risky experiments can be done through computer simulations.
Predictive maintenance focuses on preventing unexpected downtime while extending equipment life. Prescriptive maintenance approaches maintenance holistically. It prescribes the most effective maintenance action by taking into account all factors. For example, prescriptive maintenance considers data points from more sources, such as weather, finance, and accounting.
The Benefits of Prescriptive Maintenance
A reliability-centered maintenance approach gathers information from several specific processes with the objective of determining the most appropriate maintenance intervention. Some guesswork is still required, however. Prescriptive maintenance, on the other hand, allows flexibility in reliability management for plant maintenance. This creates opportunities for increased efficiency and productivity.
Here are some compelling benefits of prescriptive maintenance that go over and above what predictive maintenance has to offer:
1. Actionable Recommendations:
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance provides alerts and predictions about potential equipment failures but doesn't typically specify the exact actions to be taken.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Besides predictions, prescriptive maintenance offers specific, actionable recommendations for maintenance tasks, including steps to prevent failures.
2. Maintenance Task Automation:
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems generate alerts based on data analysis, but the decision-making and maintenance planning are often left to human operators.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Prescriptive maintenance often leverages advanced automation and artificial intelligence not only to predict issues but also to automate the decision-making process, minimizing the need for human intervention.
3. Failure Analysis:
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance offers precision by predicting potential failures based on data analysis, but it may not specify the exact cause or recommended action.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Prescriptive maintenance provides a higher degree of precision by not only predicting failures but also identifying the root causes and suggesting specific actions to mitigate them.
4. Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems improve over time by learning from data but may adapt slowly compared to prescriptive.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Prescriptive maintenance systems can continuously learn from historical data and adapt to changing conditions, refining their recommendations and becoming more accurate over time.
Prescriptive Maintenance - Key Success Factors
A prescriptive maintenance program is an important change management initiative. Organizational commitment is essential for its success. Even more important is data integrity, as data forms the bedrock of successful prescriptive maintenance.
A machine-learning model must be trained using historical data for effective prescriptive maintenance. Better quality data leads to more accurate predictions with fewer false positives. Before using the data, it may need cleaning, such as adjusting sensor values or standardizing error codes. When fed to the machine learning model, legacy data must undertake a sensitive and accurate data-cleaning process.
Higher-level information about an organization (business plan, financials, budget, capex) helps the software consider factors like repair costs, downtime, customer commitments, and even revenue targets. The model can be trained on specialized hardware, locally or in the cloud, and integrated with enterprise asset management software or CMMS to maximize its effectiveness.
Finally, companies must be open and willing to follow the model's recommendations. Because the model makes recommendations that impact operations and finances, they may cause friction and conflicts as recommendations can be cross-functional.
The Role of Software in Prescriptive Maintenance
The heart of prescriptive maintenance lies in sophisticated software that can analyze vast amounts of data and generate actionable insights. Here's how software plays a pivotal role:
- Data Integration: Prescriptive maintenance software integrates data from various sources, including sensors, equipment, and historical records, to provide a holistic view of your assets.
- Data Lake: A centralized repository that allows the banking of all structured and unstructured data at any scale. This data lake allows processing applications to be run based on system and business requirements. It can also serve as the single source of truth for all reporting.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms process the data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential issues, ensuring more accurate predictions and recommendations.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Software offers real-time monitoring, enabling you to respond immediately to changing conditions or emerging issues.
- Continuous Improvement: Prescriptive maintenance software learns from its recommendations and adapts to evolving operational conditions, ensuring ongoing optimization.
Many prescriptive maintenance software vendors are available in the market. They integrate with enterprise asset management software (EAM), CMMS, and maintenance management software. Point solutions such as work order software and preventive maintenance software may not find favor with prescriptive maintenance solutions that require a more comprehensive view of the machinery. Some examples of prescriptive maintenance software providers are IBM’s Maximo APM, Oracle Analytics Cloud, GE APM Reliability, and other smaller vendors.
Implementing Prescriptive Maintenance in Your Organization
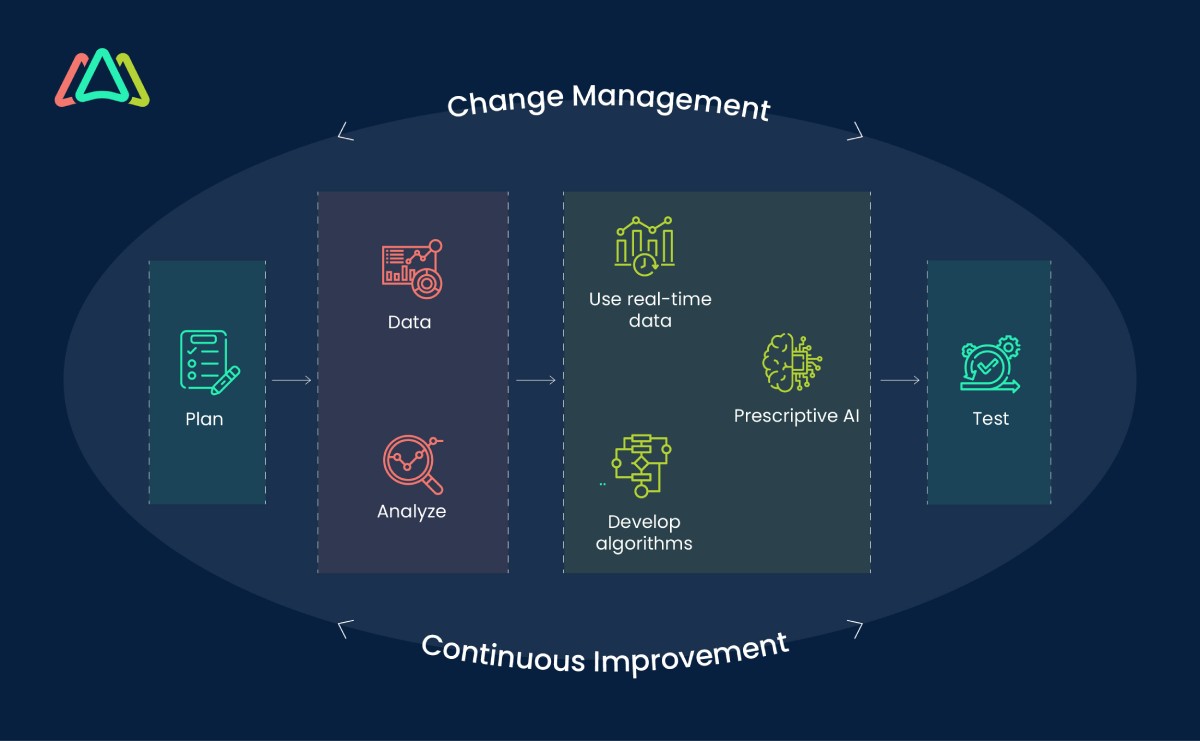
Start by evaluating the current state of your organization. Assess your current maintenance practices, software systems, and data availability. Identify areas where prescriptive maintenance could bring the most significant benefits before embarking on the implementation. To transition to prescriptive maintenance successfully, consider the following steps.
- Plan: Start with a plan by choosing a single or small sample of critical assets for a pilot project. This helps test the algorithms before fully implementing the solution.
- Data: Collect data needed for the pilot program in digital form. If available, use historical data from predictive maintenance and condition monitoring. Ensure the data collected is of high quality.
- Analyze past equipment failures to understand their causes, results, risks, and importance. This information forms the basis for prescriptive algorithms. Choose a scalable, user-friendly prescriptive maintenance software solution that aligns with your organization's needs and capabilities. Software is a must. It will only be possible to experiment with prescriptive maintenance with it.
- Use real-time data from IoT devices for prescriptive maintenance. Ensure data is available at a suitable bandwidth and capacity for analysis. Also, ensure that there is robust connectivity to enable real-time monitoring.
- Develop algorithms using information from sources like manufacturer's documentation, service history, and personnel input. Test these models before adding AI solutions.
- Prescriptive AI responds to potential failures identified by predictive algorithms. For example, a machine’s rising temperature can be addressed by reducing friction until scheduled maintenance.
- Test the initial algorithms and refine them based on specific conditions. Human oversight ensures the system works as planned and improvements are made over time.
- Include change management from the beginning to ensure smooth implementation. Train staff on new processes and procedures for better efficiency and positive outcomes. Train your maintenance teams on the new approach and communicate the benefits of prescriptive maintenance to gain their buy-in.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review the prescriptive maintenance program's effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. Prescriptive maintenance is an evolving approach. The objective is to continuously improve the prescriptive maintenance model so that follow-on prescriptions are fewer and better.
Embrace the Future
Maintenance strategies have developed from reactive to preventive, predictive, and now prescriptive. Reactive maintenance focused on fixing breakdowns, while preventive aimed to prevent failures with regular upkeep. Predictive maintenance uses sensors and software to foresee future issues, and now, prescriptive maintenance uses machine learning to recommend solutions.
Prescriptive maintenance has the potential to revolutionize the process, but it will take time to become widespread due to its complexity. It needs accurate data for training and clear communication for acceptance. This strategy may not suit small businesses or unstructured operations but should be considered for larger operations with structured processes and critical assets.
Organizations adopt different strategies based on their needs, sometimes combining using a hybrid approach. Those embracing prescriptive maintenance have an opportunity to stay ahead of the curve and become industry leaders.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





