Root Cause Analysis with CMMS Software
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often find themselves fixing the same recurring issues, treating the symptoms rather than the cause. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is useful in this situation.
Think of it as detective work for your equipment. It uncovers the hidden factors behind failures to eliminate them at the source. When combined with a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System), RCA becomes more effective, helping maintenance teams make data-driven decisions, reduce downtime, and prevent costly breakdowns.
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of RCA, why it’s essential for efficient maintenance, and how it prevents recurring failures. You’ll also discover how a CMMS enhances RCA, turning insights into action with structured processes, centralized data, and predictive maintenance strategies.
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Imagine a cracked conveyor belt in a manufacturing plant. Replacing the belt might seem like the obvious fix. However, without RCA, the true cause, whether it’s excessive tension, poor alignment, or material buildup, remains unaddressed. Left unchecked, the problem could lead to recurring failures, product contamination, or even hazardous working conditions.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used by maintenance and operations teams to uncover the underlying causes of equipment failures. Rather than just addressing surface-level issues, RCA helps identify the real factors, such as worn-out components, misalignments, or electrical malfunctions that lead to inefficiencies and costly downtime.
By implementing RCA, teams can move beyond reactive maintenance and develop long-term solutions that prevent breakdowns before they happen. Without it, recurring issues can escalate, resulting in higher costs, safety risks, and unplanned downtime that disrupts operation
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
By addressing the underlying causes of failures, RCA helps organizations improve workplace safety and meet industry regulations in the following ways:
1. Enabling Proactive Approach.
When organizations pinpoint the underlying causes of issues, they naturally start seeking improvements in other areas. This shift in perspective significantly improves an organization’s overall approach to safety, maintenance, and quality.
2. Creating Realistic Processes
After conducting RCA, teams can develop a standardized process for handling issues across the organization. While the exact steps may vary depending on the problem, RCA creates a consistent, structured approach to problem-solving that can be applied across departments and teams.
3. Reduce Downtime and Cost
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps minimize downtime by identifying and addressing the underlying issues causing these failures. By implementing long-term solutions instead of temporary fixes, maintenance departments can reduce maintenance costs, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall productivity.
4. Prevent Reoccurring Issues
RCA breaks the cycle of repeated issues by analyzing patterns, identifying contributing factors, and implementing preventive measures. This proactive approach ensures that once a problem is resolved, it doesn’t continue to resurface, leading to increased reliability, improved safety, and long-term operational stability.
5. Enhancing Compliance and Reporting
Many industries have strict regulatory requirements for safety, quality, and maintenance. RCA helps organizations maintain compliance by providing a structured method for identifying risks, documenting corrective actions, and demonstrating continuous improvement. With a clear record of past failures and resolutions, businesses can streamline audits and ensure adherence to industry standards.
How CMMS Enhances Root Cause Analysis
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a centralized platform that automates maintenance workflows, tracks asset performance, and organizes equipment failure data. CMMS software replaces spreadsheets and ad-hoc reports by providing real-time insights that help maintenance teams reduce unplanned downtime and improve asset reliability.
The following are ways CMMS enhances Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to drive more effective maintenance strategies:
1. Structured Failure Logs for Better Diagnostics
A CMMS records detailed maintenance history, making it easier to track past failures, identify recurring issues, and pinpoint patterns that indicate deeper problems.
2. Trend Analysis and Predictive Insights
With historical data and performance trends, teams can anticipate equipment failures before they happen, allowing for proactive interventions rather than reactive repairs.
3. Automated Workflows for Faster Resolutions
CMMS software streamlines RCA by standardizing corrective actions and scheduling preventive maintenance, ensuring maintenance teams follow a structured approach to issue resolution.
4. Comprehensive Context for Root Cause Analysis
When a pump fails, for example, a CMMS provides insights beyond just logging the failure. It reveals how often the breakdown has occurred, which parts were previously replaced, and whether the issue is linked to specific shifts or operating conditions.
5. Shifting from Reactive to Proactive Maintenance
By centralizing maintenance data and automating RCA processes, a CMMS helps teams identify and eliminate root causes, prevent recurring failures, and optimize long-term asset performance, leading to reduced costs and improved efficiency.
Benefits of Integrating RCA with a CMMS
1. Enhanced Problem Identification
A CMMS centralizes maintenance data, making it faster and easier to track recurring issues and identify patterns that reveal underlying root causes.
2. Streamlined Workflows & Standardized Procedures
Integrating RCA with a CMMS establishes structured problem-solving workflows, ensuring maintenance teams follow a consistent and data-driven approach to issue resolution.
For example, recurring HVAC failures often stem from missing preventive maintenance schedules. A CMMS can streamline Root Cause Analysis (RCA) by tracking historical work orders, identifying failure patterns, and automating maintenance tasks. Using the 5 Whys method and Fishbone Diagram, the root cause—missed filter replacements due to lack of automated alerts—was identified. The solution? Implement a preventive maintenance schedule and set automated alerts. A well-structured RCA workflow in CMMS ensures proactive maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns before they happen.
3. Comprehensive Failure Analysis
A CMMS enables teams to document, categorize, and analyze failure reports, providing deeper insights into recurring issues and helping pinpoint the exact sources of equipment failures.
4. Improved Communication & Collaboration
RCA insights stored in a CMMS can be easily shared across departments, improving collaboration between maintenance, operations, and management teams to ensure alignment in addressing maintenance challenges.
5. Faster Response to Equipment Failures
Automated alerts and historical RCA data allow maintenance teams to respond to failures faster, reducing diagnosis and resolution time, which helps reduce costly downtime.
6. Reduction in Emergency Repairs
By identifying and addressing root causes proactively, RCA within a CMMS minimizes the occurrence of unexpected failures, reducing the need for costly emergency repairs and promoting a more stable maintenance schedule.
Key Methods for Conducting Root Cause Analysis
RCA is a structured approach to identifying the true causes of failures. Several key methods can help teams move past surface-level issues to uncover underlying problems. When applied with a CMMS, these methods become even more effective by offering a data-driven foundation for analysis.
The 5 Whys
A simple yet powerful technique where teams ask "why" repeatedly to dig deeper into the root cause of an issue. CMMS enhances this by providing historical data, allowing teams to track recurring issues and pinpoint the true source.
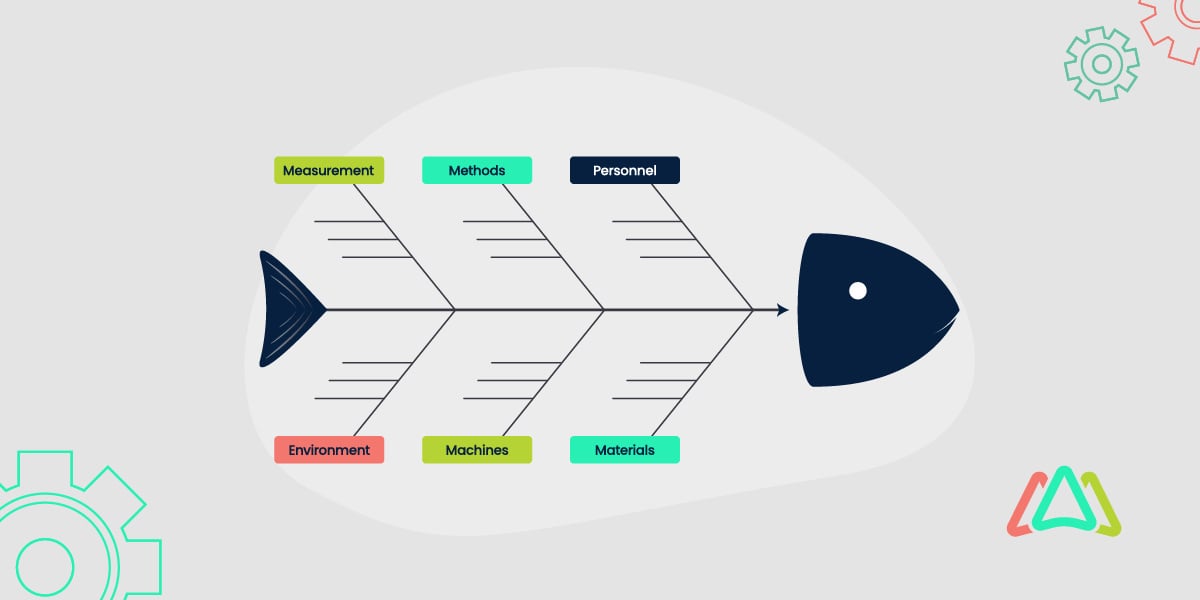
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
This method maps out potential causes across categories like human error, equipment, and processes. A CMMS can organize these potential causes, making it easier for teams to visualize patterns and identify the most significant contributors to failure.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
FMEA proactively identifies failure risks before they occur. CMMS systems support this by tracking and predicting potential failures, enabling teams to take preventive measures before an issue escalates.
Conducting Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with CMMS: A Step-by-Step Approach
Integrating Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) enhances failure analysis by providing a centralized platform for data collection, trend analysis, and proactive maintenance. The following is a step-by-step guide to conducting RCA effectively using CMMS.

1. Identifying the Problem – Logging Issues in CMMS
The RCA process begins with defining the issue and documenting its impact on operations. Using a CMMS, teams can log failures as work orders, detailing symptoms, failure frequency, and affected equipment. This structured data collection ensures no critical detail is overlooked.
2. Reviewing Past Failures and Maintenance Logs
A CMMS serves as a centralized failure repository, storing work orders, equipment history, sensor data, and maintenance logs. Reviewing this data allows teams to identify recurring problems and understand the broader context behind failures.
3. Using Reports and Dashboards to Detect Patterns
With built-in analytics, dashboards, and reports, CMMS enables teams to spot trends in equipment failures. This data-driven approach highlights common failure modes, recurring issues, and potential correlations—helping teams move from reactive troubleshooting to proactive problem-solving.
4. Identifying Root Causes – Applying RCA Methods within CMMS
Once failure patterns are identified, teams can apply structured RCA methodologies within the CMMS to pinpoint root causes. Techniques such as the 5 Whys help drill down by repeatedly questioning why a failure occurred, while the Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa) maps potential causes across factors like human error, materials, and equipment. Additionally, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) assesses risks and potential failure points before they occur.
5. Implementing and Monitoring Solutions
Once the root cause is identified, the next step is implementing corrective actions. CMMS automates workflows, assigns tasks, and ensures follow-ups are completed on time. Additionally, the system allows maintenance teams to monitor results, track performance improvements, and refine maintenance strategies based on real-time data.
6. Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
By systematically identifying failure causes and implementing data-driven corrective actions, CMMS enhances continuous improvement. Organizations can refine maintenance workflows, minimize downtime, and transition from reactive to proactive asset management.
Conclusion - Maximizing Efficiency with RCA and CMMS
Integrating Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) transforms maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive strategy. By methodically identifying and eliminating underlying causes of failures, organizations can reduce downtime, prevent recurring issues, and enhance asset performance.
A CMMS provides the structured data and analytical tools needed to execute RCA. It enables teams to track failure patterns, optimize resource allocation, and implement effective long-term solutions. This integration improves equipment reliability and cost efficiency and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
With RCA and CMMS working together, maintenance teams can move beyond short-term fixes and embrace a predictive, data-driven approach to maintenance, minimizing emergency repairs, ensuring compliance, and driving operational sustainability.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025
Introduction Due to a growing awareness of the need to combat climate change, the green ...
6 Feb 2025






