
Why More Businesses are Implementing CMMS Software
Introduction
What is it about Computerized Maintenance Management Software systems (CMMS) that makes it so attractive to a wide range of businesses across a variety of sectors? After all, before they were first introduced in the late 1960’s, companies seemed to manage quite well using standard pen and paper. As with almost everything, circumstances have changed as they continue to do so. Companies today are challenged by increasing competition, tight operations margins, economic demands and technological innovations. Traditional maintenance management strategies that did the job before aren't as effective or efficient as they once were.
To begin, CMMS software is used to manage and streamline all maintenance operations. Overall, CMMS software helps organizations efficiently manage their equipment, materias, labor and expenses and maintenance tasks, leading to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and better resource utilization. Not too long ago, CMMSs mainly catered to manufacturing operations. But today, we see the CMMS marketplace offers a wide variety of systems and options that are able to meet the needs of businesses of all types and sizes no matter what industry.
As organizations are recognizing the importance of efficient maintenance management to reduce downtime, extend asset life, and improve overall productivity, they are increasingly turning to CMMSs for their maintenance management solutions. Today, CMMS software is a burgeoning market. In 2022, the global CMMS market size was valued at USD 1.06 billion. It is also expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9% for the next seven years.
Factors Associated with CMMS Popularity
The following are some of the reasons for CMMS’s growing popularity among a wide range of businesses:
1. Improved Maintenance Efficiency
CMMS software has the ability to streamline maintenance processes, making it easier to manage work orders, track assets, and schedule preventive maintenance. In particular, a CMMS’s work order management function enables businesses to create, manage, and track work orders efficiently. It streamlines the workflow, assigns tasks to the appropriate personnel, sets priorities, and keeps all stakeholders informed about the progress of maintenance activities.The overall result is increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime, as maintenance tasks are managed more effectively.
2. Cost Savings Using Preventive Maintenance Management
By implementing CMMS software, businesses are able to optimize their maintenance operations using a preventive management approach. By using a routine scheduled approach to maintenance management, the benefit is a reduction in equipment downtime and failure. In the past, companies utilized a reactive maintenance approach, when equipment issues were attended to only when problems arose. A CMMS’s proactive approach to maintenance helps prevent costly breakdowns and extends the lifespan of assets, ultimately saving money in the long run.

3. Enhanced Asset Management
CMMS software makes it possible for businesses to keep track of their assets, including maintenance history, warranty information, and spare parts in inventory. Having this information in a report format enables better decision-making regarding asset replacement or repair.
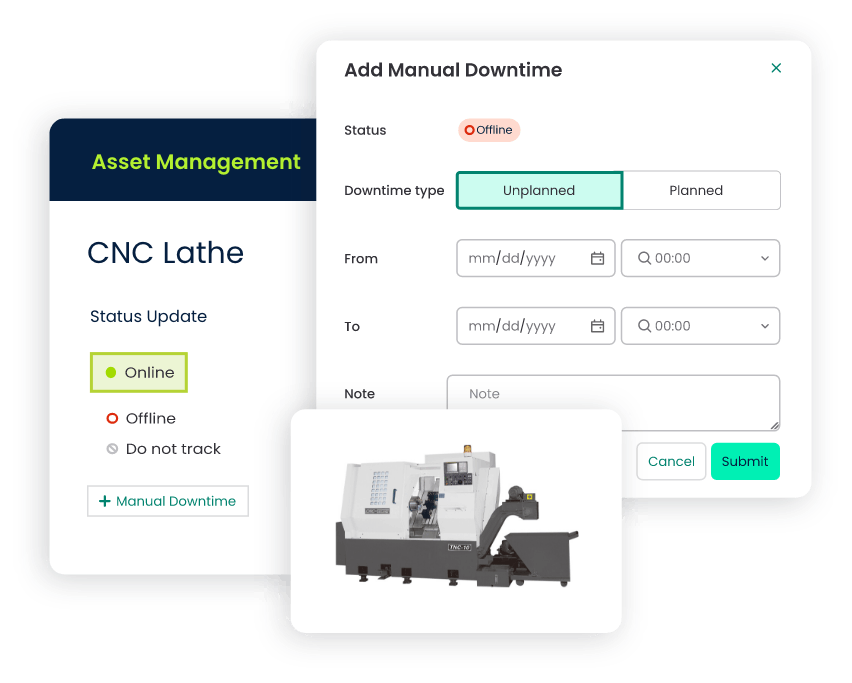
4. Inventory Control
CMMS systems often include inventory management capabilities, allowing businesses to keep track of spare parts, materials, supplies, and inventory cost. This feature helps avoid stockouts and overstocks, optimizes inventory levels, and ensures that technicians have the necessary resources readily available.
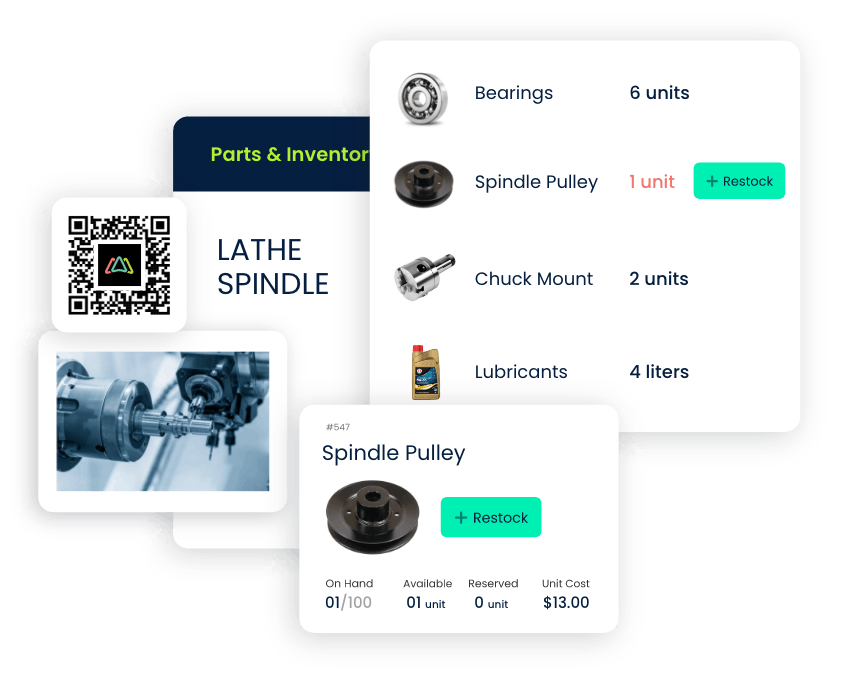
5. Regulatory Compliance
When organizations are subject to specific regulations and standards, CMMS software assists in maintaining compliance tasks by keeping detailed maintenance records, generating reports for audits, and scheduling inspections as required according to industry regulatory standards.
6. Data-Driven Insights
CMMS software reporting capabilities generate valuable data and insights related to maintenance activities, asset performance, and historical trends. Company owners and maintenance managers are then able to identify patterns, optimize maintenance schedules, analyze equipment performance and make informed decisions about asset management.
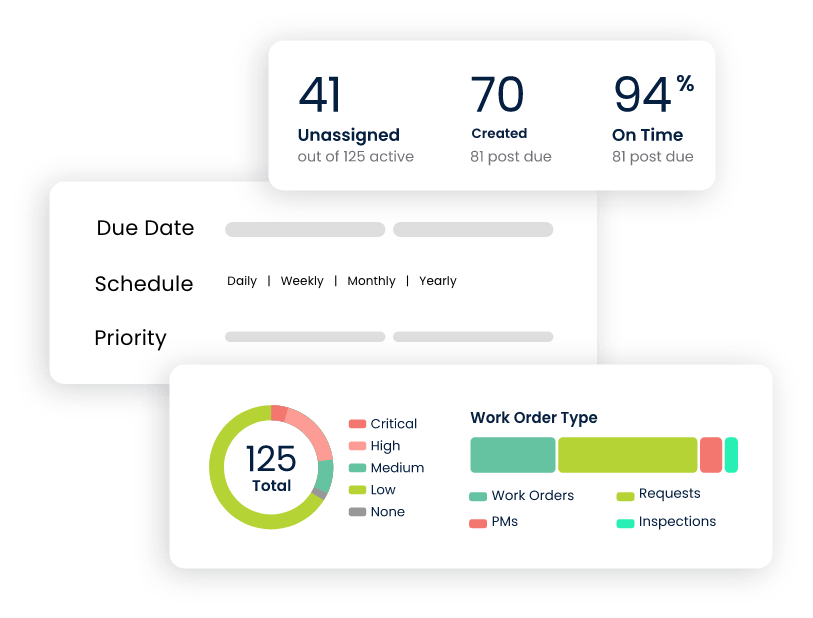
7. Remote Access and Mobility
Today’s cloud-based CMMS solutions enable remote access to maintenance data, allowing maintenance teams to access information and submit work orders from anywhere, improving collaboration and responsiveness. Previously, work orders that at times took hours to days to process, can now be initiated in minutes.
The wide adoption of smartphones and tablets have made mobile maintenance and work order management the norm. With Work Order Apps, users are notified of assigned work and requests in real-time and these can be updated in seconds, on-site while completely eliminating any paper trail. Mobile CMMS makes it easy to remotely create and update work orders, add images, scan QR codes and more.
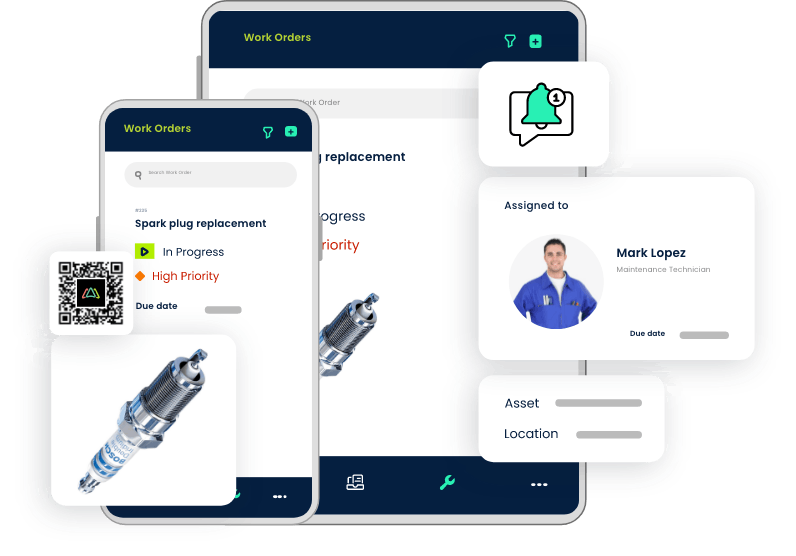
8. Integration and Compatibility with IoT
loT is an acronym for the Internet of Things. In the maintenance management world, this relates to equipment with sensors that are able to send real time operations data from it to a CMMS. It can also integrate other business software such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). This relatively new capability is a valuable tool in predictive maintenance which identifies issues before they cause significant problems. CMMS integration enhances data flow, facilitates automated processes, and provides a comprehensive view of maintenance operations.
9. User-Friendly Interfaces
Since not everyone is computer savvy, more recently developed CMMS solutions come with user-friendly interfaces, making it easier for maintenance teams to adopt and feel confident when using the software effectively.
10. Scalability
Given the previously noted challenges that companies face, CMMS software is able to accommodate the growing and changing needs of both small businesses and larger enterprises without having to purchase another system. As well, CMMS providers have been tailoring their offerings to meet the specific needs of different industries. Where CMMS software was primarily targeted to larger enterprises in the past, today’s CMMS are priced and offer functionality that is suited for SMB and enterprise businesses. This customization has attracted more customers seeking specialized maintenance solutions for their particular sectors. The scalability and industry-specific Solutions of CMMS makes it a versatile solution across industries.
11. Customer Satisfaction
Without a doubt, efficient maintenance processes lead to better functioning assets and equipment, resulting in improved product or service quality. This strengthens customer satisfaction and loyalty.
12. Sustainability Initiatives
Apart from optimizing the lifespan of assets, environmental considerations are also becoming an increasing concern. CMMS software can help businesses implement sustainability initiatives by optimizing maintenance practices, and reducing waste as well as potentially toxic emissions while prolonging the life of assets.
13. Competitive Advantage
CMMS takes the time and guesswork out of conducting efficient and effective maintenance management tasks. Businesses that adopt CMMS software gain a competitive edge by reducing downtime, saving costs, and improving overall operational efficiency compared to their competitors who might still rely on traditional maintenance methods.
Business Sectors Using CMMS
If you’re still unsure if your business can benefit from CMMS software, the following is a list of business sectors that have embraced its capabilities in their maintenance operations:
1. Manufacturing Companies
Manufacturing plants were the first to make the shift from traditional maintenance management approaches to CMMS. Having a wide range of equipment and machinery requiring regular maintenance and monitoring made CMMS software an attractive solution. CMMS helps manufacturers schedule preventive maintenance, track spare parts inventory, and reduce unplanned downtime.
2. Facilities Management Companies
Businesses that specialize in commercial facilities maintenance, such as office buildings, hospitals, universities, and shopping malls, use CMMS to manage maintenance tasks for various systems like HVAC, elevators, lighting, plumbing, and more. The efficiency and time saving benefits are two of the reasons these companies choose CMMS as their preferred maintenance management solution.
3. Energy and Utilities
Power plants, water treatment facilities, and other utilities often use CMMS to keep their critical infrastructure running efficiently, ensuring reliable energy production and distribution. Since so many people rely on these essential systems, CMMS makes consistent and reliable delivery of its services possible.
4. Transportation and Logistics
Transportation companies with fleets of vehicles, airlines, and shipping logistics firms use CMMS to manage maintenance for their vehicles and transportation assets. CMMS can prevent and reduce unnecessary delays due to malfunctions in any of these assets.
5. Healthcare Institutions
Hospitals and healthcare facilities rely on Healthcare CMMS to ensure the smooth operation of medical equipment and facilities, adhering to strict compliance and safety standards.
6. Hospitality Industry
Hotels and resorts utilize CMMS to manage maintenance for guest rooms, HVAC systems, elevators, and other amenities. Having well functioning facilities is a key factor in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Download the Preventive Maintenance Checklist for your HVAC System
Image: HVAC Systems
7. Municipalities and Government Agencies
Local governments and public entities use CMMS to manage maintenance for public infrastructure like roads, bridges, water supply, and sewage systems. CMMS’s ability to scale and integrate with this large network of organizations makes it a valuable resource.
8. Food and Beverage Industry
Restaurants, food processing plants, and breweries employ CMMS to manage maintenance for production equipment and keep their facilities compliant with hygiene and safety regulations. CMMS can accommodate maintenance management tasks for single operations all the way up to large facilities and country wide chain food and beverage organizations.
9. Oil and Gas
Companies in the oil and gas industry adopt CMMS to ensure the efficient maintenance of drilling rigs, pipelines, and refineries, reducing downtime and increasing safety. Just like companies in the manufacturing industry sector, oil and gas facilities have many pieces of sophisticated equipment of various kinds that benefit from the sophisticated and robust CMMS features and capabilities.
10. Educational Institutions
Schools, colleges, and universities use CMMS to manage maintenance for their buildings, classrooms, and equipment. CMMS can be scaled to the needs of small colleges, universities as well as entire school districts.
11. Data Centers
Data centers rely on CMMS to manage the maintenance and uptime of their critical infrastructure, including servers, cooling systems, and power supply. The sensitivity of data center equipment makes the ongoing maintenance capabilities of CMMS an excellent choice.
Conclusion
Businesses of all sizes and across numerous sectors are increasingly choosing to implement CMMS software to optimize maintenance processes, reduce costs, improve asset management, enhance data-driven decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries. Given these capabilities, the previously noted projected growth trend for CMMS is sure to be realized.
When considering a CMMS, it’s important to note that its features and requirements may vary depending on the size, complexity, and unique needs of each business. With many options available in the CMMS marketplace, it is essential that you begin with conducting a thorough evaluation and then choosing a solution with the CMMS features that best fit your organization’s specific needs and requirements.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





