
5 Tips for Getting Maintenance Technicians to Use CMMS Mobile Apps
According to statistica.com, currently over 91% of Americans (310 million) own smartphones. With this widespread use of smart mobile devices, one might assume that maintenance technicians would naturally latch onto using the CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) mobile apps. Considering we’re in an age of apps for everything, this should be a “no-brainer.” Interestingly, this isn’t always the case primarily because some maintenance technicians find CMMS mobile apps a nuisance or prefer traditional manual work order management methods. As a result, CMMS mobile apps are underutilized, and their benefits fall short of what’s expected.
Since mobile CMMS can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of maintenance operations, it’s in company owners’ and managers’ best interests to find ways to encourage maintenance technicians to use mobile apps as part of their routine maintenance processes. In this article, we’ll first look at some of the standard methods of encouraging CMMS mobile app adoption and then explore five unique tips that will make user adoption even more enticing.

Common Ways to Increase CMMS Mobile App Adoption
Provide Training and Support
Offering comprehensive training sessions to familiarize technicians with the CMMS mobile features and functions is an essential starting point for encouraging user adoption. Maintenance technicians must understand how it works to see the benefit of using a CMMS mobile app. In other words, they must learn how to create work orders, update asset information, and record maintenance activities.
Training and onboarding do not have to be boring. These can be done in different formats, making meeting different learning styles and schedules easy and convenient. Examples include offering webinars, video tutorials, and workshops. CMMS mobile apps have scaled-down functionality compared to the desktop versions. Learning how to use the mobile app is pretty easy if the app provider applies best practices for UX. Most app providers include easy-to-access support and knowledge base resources directly from the app or their website. Training and onboarding for CMMS mobile apps is less involved than the desktop version of the same CMMS software.
Highlight Benefits and Convenience
When maintenance technicians understand the benefits and convenience of using a CMMS mobile app, they’re more likely to adopt it. Understanding that using the CMMS mobile app allows them to access critical information in real-time, receive notifications for urgent tasks, and submit updates from anywhere in the facility makes it clear that using the app is worthwhile, especially since it makes their jobs easier. By showcasing how the app streamlines their workflow, reduces paperwork, and improves response time, the CMMS mobile app will be viewed as a way to save time and increase efficiency.
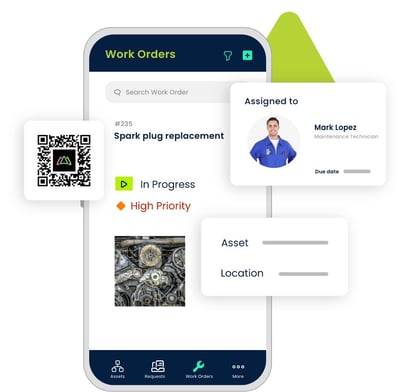
Streamline Workflows
As noted earlier, one of the roadblocks to user adoption of a CMMS mobile app is that it is seen as a nuisance. Techs will likely view the new initiative as extra work without proper training, orientation, and demonstrating the benefits. An app that is confusing or requires too many steps to get what you want will not appeal to already wary maintenance technicians. Before implementing the mobile technology into the maintenance team’s processes, determine how to configure the work order app best so that it streamlines the maintenance workflows. Ensure that work orders are auto-assigned to the right technicians, QR codes are adhered to assets, parts bins, locations, and other items, and notifications are enabled correctly. Turn off any functionality that is not necessary. Eliminating unnecessary steps and automating routine tasks to save time and effort will encourage technicians to use the CMMS mobile app often and consistently.
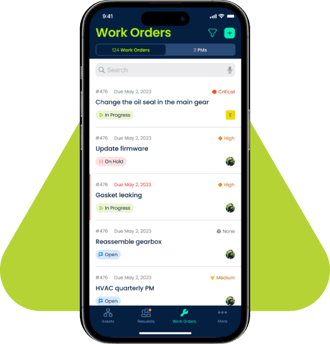
Incorporate User Feedback
Feeling heard and understood is crucial for achieving user buy-in to a CMMS mobile app. Company owners and maintenance managers should seek technicians' feedback about their mobile app experiences. Establish a feedback mechanism to make the process easy. One way to do this is by creating feedback forms that make gathering technician suggestions and concerns easy. Technicians can comment on the app's usability, performance, and features. Company owners can use their feedback for continuous improvement by considering their suggestions and implementing relevant changes to address their concerns. Involving maintenance technicians in the customization and optimization process can foster a sense of ownership and investment in the tool.
Five Unique Tips to Enhance Maintenance Technicians’ Adoption of CMMS Mobile Apps
Beyond the commonly used ways of encouraging user adoption of CMMS mobile apps just described, here are five unique tips to enhance their routine and consistent use.
Set Clear Expectations and Encourage Accountability
Knowing what is expected of maintenance technicians is one way to motivate them to follow through. This is especially true when encouraging maintenance technicians to routinely and consistently use a CMMS mobile app. Communicate the expectations for app usage and the benefits it brings to the team and the organization. Make it clear that using the CMMS mobile app is a standard practice and not optional.
Another aspect of establishing clear expectations for using the CMMS mobile app is providing maintenance technicians with objective and precise feedback on the benefits of doing so. This can be done by using performance analytics based on their CMMS mobile app usage. One way to do this is by setting up a key performance indicator (KPI) dashboard where technicians can see their performance metrics. This helps them track their productivity and identify areas for improvement.
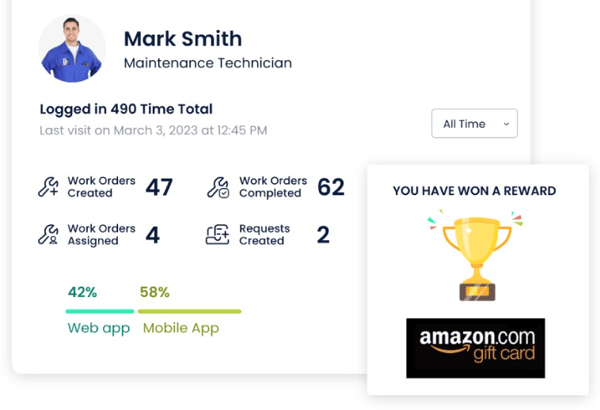
Gamification and Reward Incentives
Technicians' ability to observe firsthand the benefits of using a CMMS mobile app by monitoring their KPIs is a form of intrinsic reinforcement that encourages continued use. Tangible and extrinsic rewards can also achieve and enhance this same result. Since rewards are a powerful way of increasing targeted behaviors, they can also be used to incentivize continued app use. Company owners can implement a system that recognizes maintenance technicians for their performance, completion of tasks, or for providing valuable input. By way of an example, they can create a point system or badges for completing tasks or entering data on the app. Rewards can take any number of forms, including gift cards, extra time off, or placing a technician’s name on a top user's plaque.
The reward process can be further elevated by adding a gamification or incentive element to motivate technicians to adopt the CMMS mobile app. Combining fun and rewards can lessen technician hesitation while creating healthy competition among team members.
Goal Setting
Setting reasonable goals and rewarding technicians for achieving or exceeding them picks up on what was just described. Establishing a work order completion goal when using a CMMS mobile app adds another competitive element to maintenance operations and lets technicians see how it can enhance efficiency. Some CMMS systems can tabulate this information in a graphic format.
Customized User Experience
The CMMS mobile app interface can be tailored to match individual preferences, operating styles, and job roles. Personalizing settings makes it more user-friendly and inviting. Customizing the interface and features to suit their needs and tasks encourages maintenance technicians to take ownership of the mobile app’s look and operations. It also demonstrates that a CMMS mobile app need not be a one-size-fits-all experience.
Company Supplied Mobile Devices
Company-supplied mobile devices are a win-win for both maintenance technicians and company owners. For maintenance technicians, not having to use their own mobile devices alleviates concerns regarding added fees, damage, and general wear and tear on their devices. For company owners, supplying mobile devices to maintenance technicians offers increased security and control over what the devices are used for. By providing team members with mobile devices, company owners have greater control over their operation and functioning. At the same time, owners and maintenance managers can be confident that business software and data are secure. The result is less stress and frustration for all.
A smooth transition to CMMS mobile apps requires patience and ongoing support. This is a process that will take time to happen. Company owners and maintenance managers can expect a range in maintenance technicians’ willingness to use the CMMS mobile app frequently and consistently. Beyond offering practical training and onboarding, stressing the app’s value and benefits, streamlining workflows, and encouraging feedback to improve its functioning, leaders are challenged to find ways for maintenance technicians to buy into using new technology. Adding elements such as setting expectations and goals, gamification and rewards, and company-supplied devices adds commitment, fun, and competitiveness while reducing many reasons for maintenance technicians’ initial wariness. In the end, maintenance technicians will feel comfortable and confident using it when standard ways of encouraging users' adoption with those that add commitment, fun, competitiveness, and intrinsic value are combined.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





