BENEFITS OF CMMS INTEGRATION
By connecting the CMMS with other software systems and devices, businesses can unlock powerful advantages that drive efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. Here are some key benefits of CMMS integration:
Centralized Data Management
Integration allows for the consolidation of data from various systems into a central CMMS database. This provides a single source of truth for maintenance-related information, such as asset data, work orders, inventory, and maintenance history. Centralized data management eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces data duplication, and ensures data accuracy and consistency.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reliability
CMMS integration promotes data accuracy and reliability by ensuring consistent information across different platforms. When information is shared and synchronized between systems, there is a reduced risk of data discrepancies or outdated records. Real-time data updates through integration enable maintenance personnel to access the most up-to-date information on assets, maintenance history, inventory, and more. Accurate and reliable data empowers better decision-making, improved planning, and effective resource allocation.
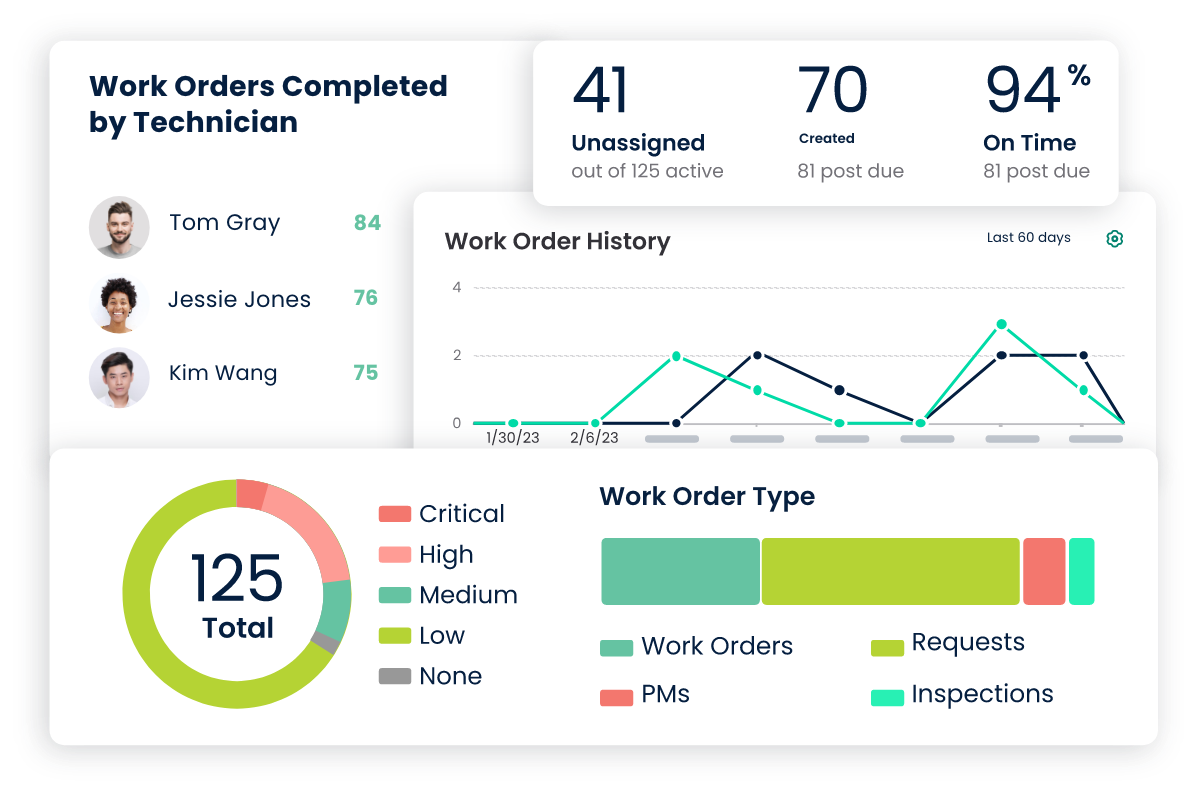
Real-Time Visibility and Reporting
Managers and stakeholders can access detailed reports, key performance indicators (KPIs), and analytics through a centralized dashboard. Real-time insights allow them to monitor maintenance operations, track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. With CMMS integration, organizations can proactively manage maintenance tasks, prioritize work orders, and optimize resource allocation based on accurate and timely information.
Automation of Maintenance Processes
CMMS integration enables the automation of various maintenance processes, resulting in significant time savings and improved productivity. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) devices, sensors, and equipment allows for automated data collection, remote monitoring, and preventive maintenance scheduling. When critical parameters, such as equipment performance or asset conditions, fall outside predefined thresholds, CMMS integration can trigger automated alerts, work orders, or notifications to maintenance teams. Automation reduces manual intervention, increases responsiveness, and helps prevent equipment failures or costly downtime.
Cost Savings through Optimized Resource Allocation
By integrating CMMS with financial or resource management systems, organizations can optimize resource allocation and achieve cost savings. Real-time data and analytics provide insights into maintenance costs, equipment downtime, inventory levels, and resource utilization. This enables proactive planning, efficient scheduling of maintenance activities, and effective inventory management. These measures lead to reduced maintenance costs, improved asset lifespan, and improved ROI for CMMS investments.
Improved Collaboration and Compliance
CMMS integration enhances collaboration and communication between maintenance teams and other departments, such as finance. Integrating the CMMS with financial systems or ERP software enables seamless coordination between maintenance operations and financial management. It ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations by integrating with compliance management systems. This streamlines documentation, tracks compliance activities, and generates audit reports, simplifying the compliance process and minimizing non-compliance risks.
By leveraging the power of integration, organizations can elevate their maintenance management practices, achieve operational excellence, and maximize the value of their CMMS investment.