- CMMS
- Industry
- CMMS Software for the Food & Beverage Industry
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Overview of Food and Beverage Processing Plants
Food processing facilities are complex environments where the synthesis of raw materials into consumable products demands a high level of precision and efficiency. Inherent in this complexity is the need for meticulous maintenance to ensure the seamless operation of the facility and equipment, adherence to safety standards, and the production of quality food products.

Maintenance of Processing Equipment
Regular Inspections
- Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled inspections to identify and rectify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns.
- Calibration Checks: Ensuring accuracy in equipment settings for optimal performance.
Cleaning and Sanitization
- Cleaning Protocols: Thorough cleaning of processing equipment to prevent contamination.
- Sanitization Procedures: Application of sanitizing agents to eliminate harmful microorganisms.
Emergency Repairs
- Downtime Management: Swift response to unexpected breakdowns to minimize production disruptions.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts for prompt replacements.

Facility Infrastructure Maintenance
Building Maintenance
- Roof and Structural Inspections: Ensuring the integrity of the facility's structure.
- HVAC Systems: Regular maintenance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for optimal climate control.
- Plumbing and Electrical Systems: Regular maintenance of all critical plumbing and electrical systems to ensure that the facility operates as expected and prevents breakdowns.
Utilities and Services
- Water and Energy Management: Efficient use and maintenance of water and energy systems.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal and recycling of waste generated during production.
Safety Systems
- Fire Safety Inspections: Regular checks of fire suppression systems and emergency exits.
- Security Systems Maintenance: Ensuring the functionality of security cameras and access control systems.
Maintenance Challenges for Food & Beverage Processing Plants
|
Problem |
Solution |
|
|---|---|---|
1. Corrosion and Rust in Processing Equipment |
The constant exposure to water, cleaning agents, and acidic ingredients can lead to corrosion and rust in processing equipment, affecting both performance and hygiene. |
Implementing regular inspections, using corrosion-resistant materials, and applying protective coatings can mitigate these issues. |
2. Sanitation and Cleanliness Compliance |
Maintaining a high level of cleanliness is paramount in food manufacturing. Meeting sanitation standards while minimizing downtime poses a significant challenge. |
Implementing stringent cleaning schedules, utilizing food-grade lubricants, and integrating automated cleaning processes can help ensure compliance. |
3. Pest Control in Production Areas |
The presence of pests poses a threat to both product quality and safety. Traditional maintenance approaches may not be sufficient to combat this persistent challenge. |
Implementing integrated pest management programs, regular inspections, and employing preventive measures such as sealing entry points are essential. |
4. Equipment Downtime Impacting Production |
Unplanned equipment breakdowns can result in significant downtime, affecting production schedules and increasing operational costs. |
Adopting predictive maintenance strategies, utilizing advanced monitoring technologies, and maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts can minimize downtime. |
5. Compliance with Evolving Regulatory Standards |
The food industry is subject to ever-evolving regulatory standards. Staying compliant with these standards and adapting to changes pose ongoing challenges. |
Regular training for maintenance and production teams, maintaining meticulous documentation, and leveraging CMMS for regulatory tracking can assist in compliance. |
6. Managing Complex Supply Chains |
Food manufacturing facilities often deal with intricate supply chains, making it challenging to ensure a continuous and reliable flow of raw materials. |
Collaborative communication with suppliers, implementing inventory management systems, and building strategic partnerships can help streamline the supply chain. |
7. Energy Consumption and Sustainability |
Balancing the need for energy-intensive production processes with sustainability goals poses a unique challenge in food manufacturing. |
Implementing energy-efficient equipment, adopting sustainable practices, and regularly assessing energy consumption can contribute to a more sustainable operation. |
8. Aging Infrastructure and Equipment |
Aging machinery and infrastructure may become more prone to breakdowns, leading to increased maintenance requirements. |
Implementing a proactive replacement strategy, conducting regular assessments of equipment health, and investing in modern technologies can mitigate this challenge. |
Why Traditional Maintenance Approaches Fall Short
Traditional maintenance approaches often prove inadequate in addressing the unique challenges faced by food and beverage processing plants. The dynamic nature of the industry, stringent regulatory requirements, and the need for precision make it evident that relying solely on conventional methods can lead to inefficiencies and increased risks. Here's an exploration of why traditional maintenance falls short in addressing the specific challenges outlined:
|
Challenge |
Traditional Approach |
Limitations |
Suggested Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
1. Reactive Nature |
Relying on reactive responses to breakdowns. |
Unplanned downtime, increased costs, potential quality issues |
Shift to a proactive maintenance strategy, identifying and addressing issues before failures occur. |
2. Manual Inspection and Record-Keeping |
Reliance on manual inspections and record-keeping. |
Inaccurate data, missed inspections, compliance gaps |
Implement digital solutions like CMMS for automated scheduling, data recording, and compliance tracking. |
3. Lack of Predictive Capabilities |
Absence of predictive capabilities to foresee equipment failures. |
Increased reliance on reactive maintenance, higher downtime, and costs |
Integrate predictive maintenance technologies, such as IoT sensors and data analytics. |
4. Limited Focus on Regulatory Compliance |
Insufficient tools for continuous compliance with changing regulations. |
Increased risk of non-compliance, penalties, and reputational damage |
Implement digital systems for real-time monitoring, documentation, and reporting. |
5. Inefficiencies in Supply Chain Management |
Inadequate solutions for managing supply chain complexities. |
Inconsistent supply, production delays, increased costs |
Integrate maintenance strategies with supply chain management, foster collaboration, and leverage technology for visibility. |
6. Insufficient Emphasis on Energy Efficiency |
Lack of prioritization for energy efficiency. |
Increased energy consumption, higher costs, sustainability challenges |
Incorporate energy-efficient equipment, conduct energy audits, and adopt sustainable practices in maintenance. |
7. Overlooking Aging Infrastructure Challenges |
Failure to address challenges posed by aging infrastructure. |
Increased risk of breakdowns, higher maintenance costs, safety hazards |
Implement a proactive asset management strategy, conduct regular assessments, and plan for infrastructure upgrades. |
Benefits of CMMS for Food Manufacturing Facilities
Improved Equipment Reliability
Reduced Downtime:
- CMMS empowers proactive maintenance strategies, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
- Real-time monitoring and predictive capabilities enable swift responses to emerging issues, significantly reducing downtime and ensuring continuous production.
Increased Equipment Lifespan:
- Scheduled maintenance tasks and asset performance tracking contribute to the longevity of equipment.
- CMMS facilitates a systematic approach to maintenance, ensuring that assets are consistently cared for, thereby extending their operational lifespan.
Enhanced Preventive Maintenance
Scheduled Inspections and Maintenance Tasks:
- CMMS automates the scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks, ensuring regular inspections and routine maintenance.
- This proactive approach reduces equipment failures, contributing to a more stable and reliable production environment.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
- CMMS provides a centralized platform for documenting and tracking maintenance activities.
- Ensures adherence to stringent regulatory standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance during audits and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
Inventory and Asset Management
Efficient Spare Parts Management:
- CMMS optimizes inventory management by automating reorder processes based on usage patterns and maintenance schedules.
- Ensures that critical spare parts are readily available, minimizing the risk of stockouts and streamlining the equipment repair process.
Tracking and Managing Critical Assets:
- CMMS facilitates the tracking and management of critical assets through a centralized database.
- Provides insights into asset health, maintenance history, and performance metrics, enabling informed decision-making and efficient utilization of assets.
Click Maint CMMS Features for Food & Beverage Industry
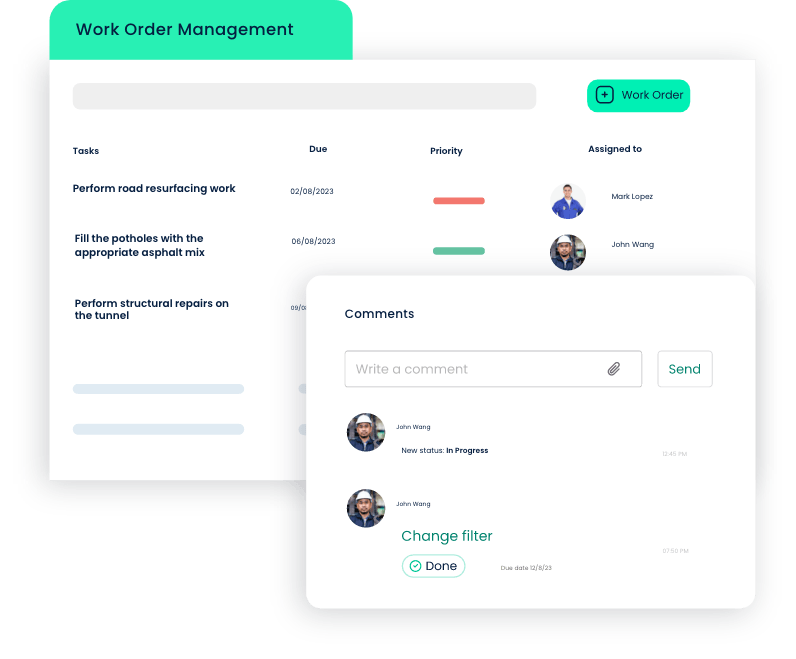
Work Order Management
- Streamlining Maintenance Tasks: Click Maint provides an intuitive interface for creating, assigning, and tracking maintenance tasks, ensuring a seamless workflow and minimizing response times.
- Real-time Monitoring: The CMMS offers real-time visibility into the status of work orders, enabling faster response times and time to complete.
Equipment Tracking and Monitoring
- Asset Performance Metrics: Click Maint allows for the tracking of critical asset performance metrics, such as runtime, failure rates, and maintenance history, reducing downtime and enabling data-driven decision-making.
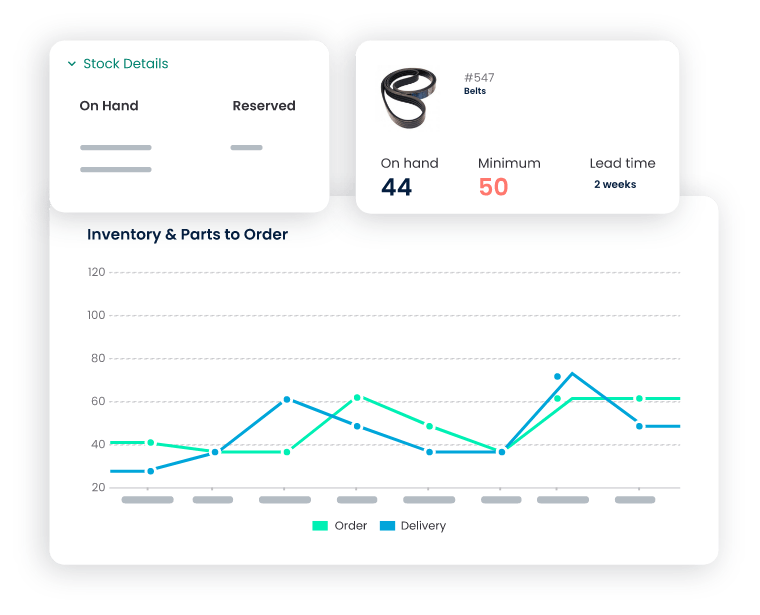
Inventory Management
- Minimizing Stockouts: Click Maint optimizes inventory management, automating reorder processes based on usage patterns and maintenance schedules to prevent stockouts of critical spare parts.
- Cost-effective Procurement: The CMMS provides insights into vendor performance, facilitating informed decisions for cost-effective procurement of spare parts and reduced wait time.
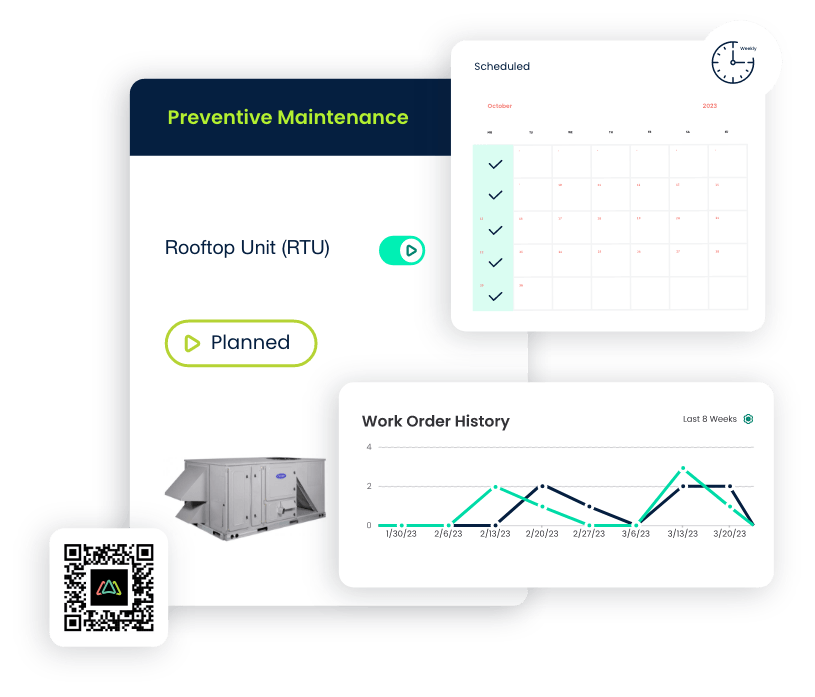
Preventive Maintenance
- Scheduled Inspections: Click Maint automates the scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks, including regular inspections essential for maintaining hygiene standards in the food and beverage industry.
- Regulatory Compliance: The CMMS supports compliance with food safety regulations by automating documentation processes and ensuring a comprehensive record of maintenance activities for regulatory audits.
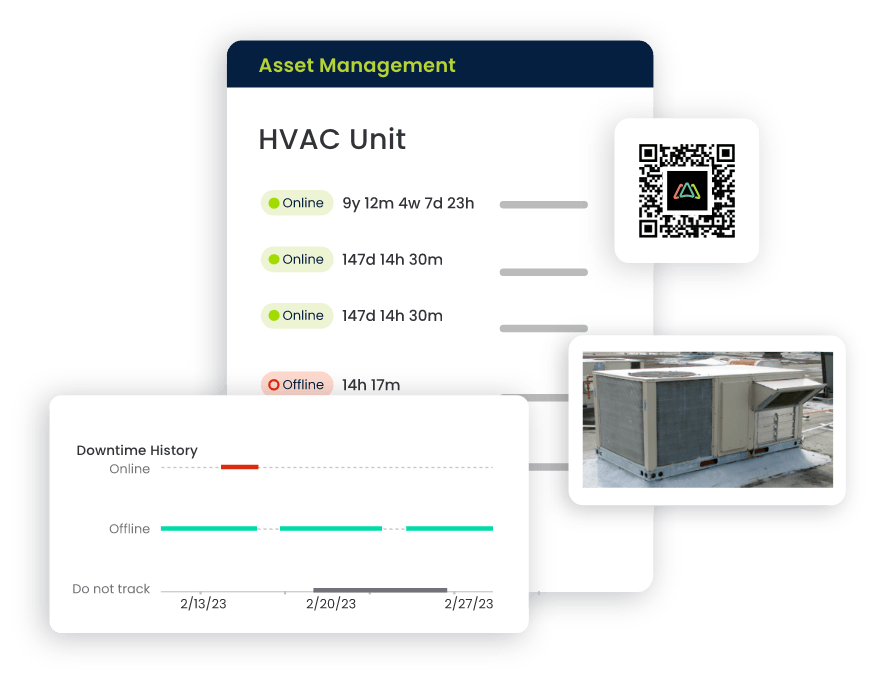
Asset Management
- Efficient Spare Parts Management: Click Maint streamlines the management of spare parts, ensuring efficient tracking and minimizing downtime associated with equipment repairs in food processing machinery.
- Tracking Critical Assets: The CMMS facilitates centralized tracking of critical assets, providing insights into asset health, maintenance history, and performance metrics essential for ensuring food safety.
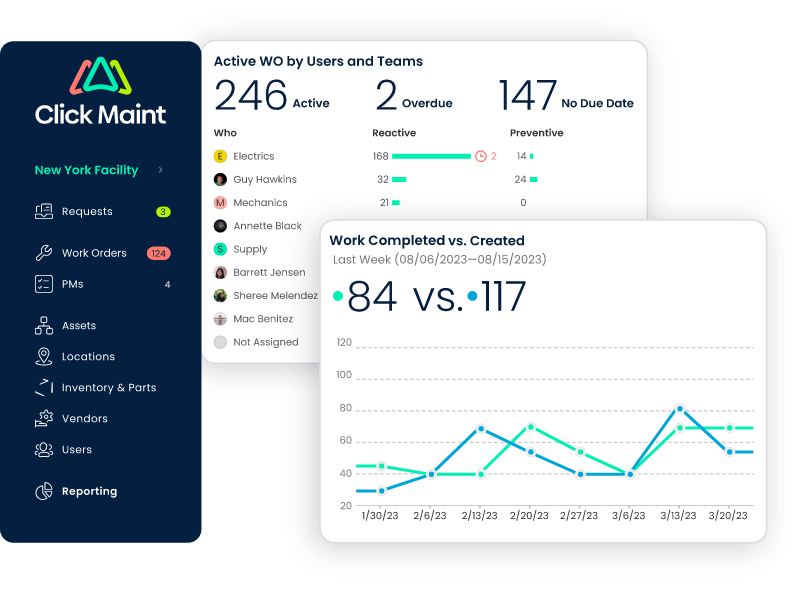
User-friendly Interface
- Intuitive Navigation: Click Maint boasts a user-friendly interface, making it easy for maintenance teams to navigate and utilize the system efficiently.
- Customizable Dashboards: Tailored dashboards allow users to configure views based on specific needs, providing a personalized and efficient user experience.
CMMS Mobile: Transforming Food and Beverage Manufacturing Maintenance Operations
On-the-Go Work Order Management
Click Maint’s CMMS mobile app empowers maintenance teams to create, assign, and update work orders on the go. This real-time capability ensures swift responses to emerging issues, minimizing downtime and optimizing production efficiency.
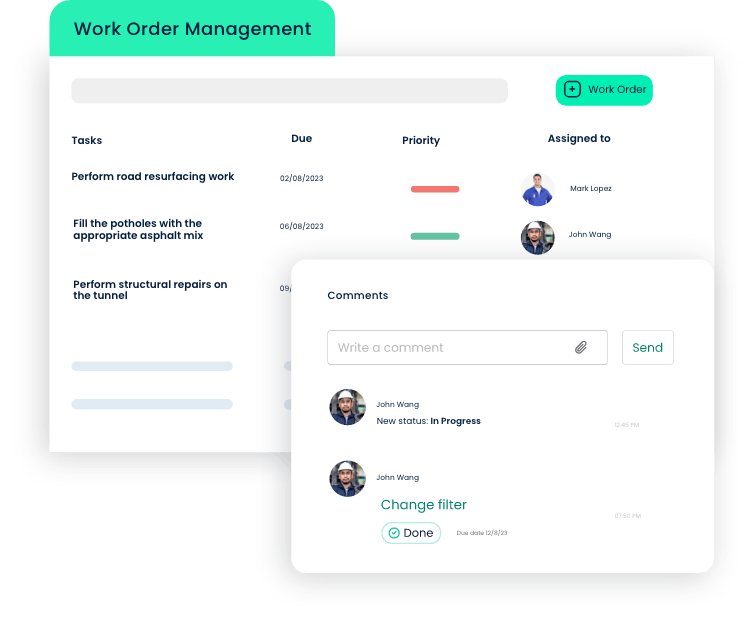
Efficient Asset Monitoring
Mobile CMMS allows maintenance teams to conduct equipment inspections and record data instantly using mobile devices. This agility facilitates quick identification of potential issues, supporting preventive maintenance efforts and reducing the risk of equipment failures.
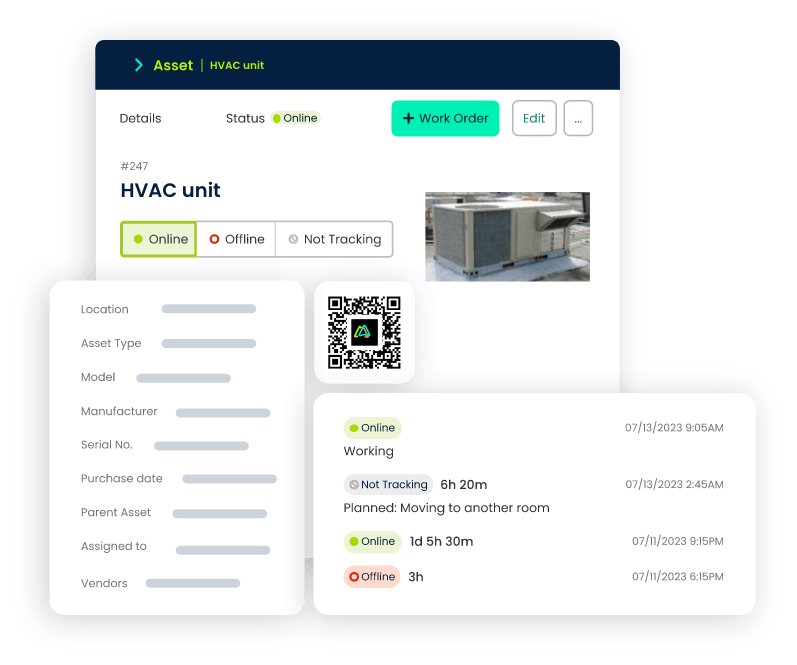
Spare Parts Accessibility
Mobile CMMS enables maintenance staff to access the inventory database remotely. This feature ensures that critical spare parts are readily available, minimizing equipment downtime due to stockouts and streamlining the maintenance process.




Collaboration and Communication
Mobile CMMS fosters real-time communication among maintenance teams. Team members can instantly share updates and insights and collaborate on resolving issues, promoting a collaborative and responsive maintenance culture.
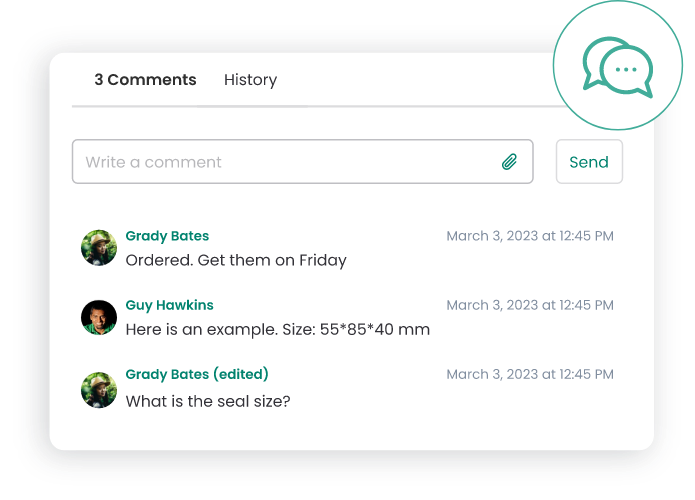
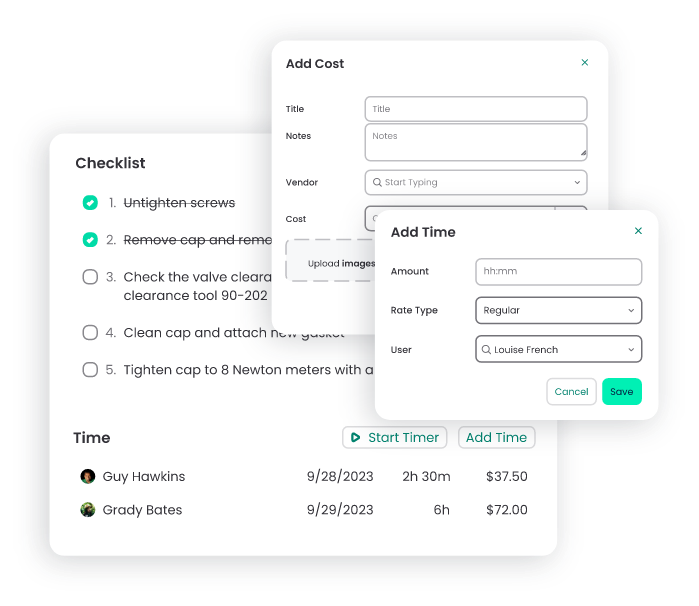
Instant Data Entry
Mobile CMMS eliminates the need for manual data entry backlogs by enabling instant recording of maintenance activities. This not only improves data accuracy but also provides real-time insights into equipment health and overall maintenance performance.
Remote Access to Maintenance Information
Mobile CMMS ensures that remote teams, such as field technicians or staff on different shifts, have access to critical maintenance information. This inclusivity enhances overall visibility and ensures that maintenance efforts are coordinated effectively.
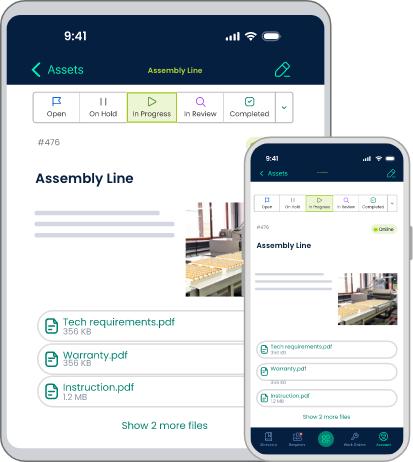



Digital Documentation
Mobile CMMS promotes a paperless approach to maintenance documentation. Electronic records of inspections, repairs, and compliance activities reduce the risk of errors, enhance traceability, and support compliance with regulatory standards.
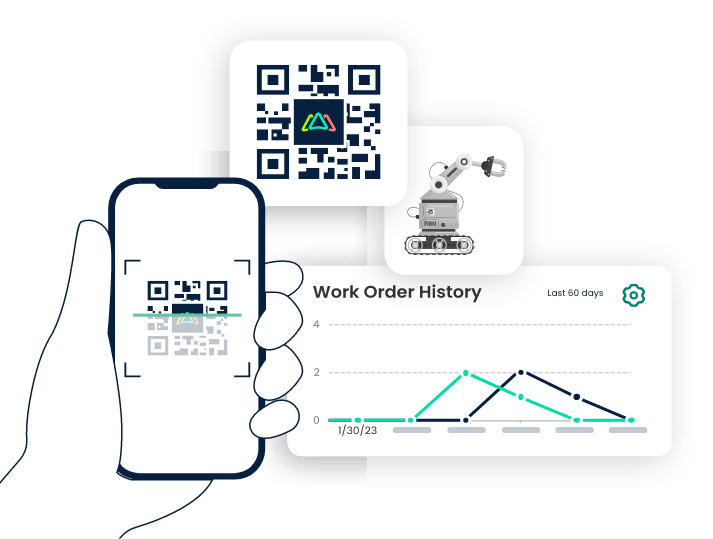
Efficient Asset Identification
Mobile CMMS often integrates with QR code technology, allowing for quick and accurate identification of assets. This feature streamlines asset tracking and facilitates a faster response to maintenance needs.
Intuitive Mobile Interface
CMMS mobile applications feature user-friendly interfaces, ensuring that maintenance teams can easily navigate and utilize the system while on the move.



Discover How CMMS Makes it Easy to Access Records and Maintenance History.

CMMS Best Practices for Food & Beverage Processing
Configure CMMS Specific for Industry
- Tailor CMMS to the unique needs of the food industry, incorporating features that address regulatory requirements and specific maintenance challenges in food manufacturing.
- Work closely with CMMS providers to configure workflows, preventive maintenance schedules, and reporting functionalities to align with food safety standards and production demands.
Comprehensive Training Programs
- Invest in thorough training programs to equip maintenance teams with the skills and confidence to effectively use the CMMS.
- Provide hands-on training sessions that cover all aspects of CMMS usage, emphasizing the importance of accurate data entry, work order management, and utilization of industry-specific features. Get them to talk to support and access our knowledge base.
Real-time Data Entry and Updates
- Emphasize the importance of real-time data entry to ensure the accuracy and relevance of maintenance records.
- Encourage maintenance teams to use mobile CMMS capabilities for instant data entry and updates. This practice enhances the precision of asset records, maintenance history, and compliance documentation.
Integration with Quality Management Systems (QMS)
- Integrate CMMS with Quality Management Systems to create a seamless workflow that aligns maintenance efforts with quality control measures.
- Collaborate with QMS providers to establish an integrated system that facilitates the exchange of data between maintenance and quality management functions.
- This integration ensures a holistic approach to maintaining both equipment and product quality.
Regular Audits and Performance Reviews
- Conduct regular audits and performance reviews to assess the effectiveness of CMMS usage.
- Periodically review data accuracy, completeness, and adherence to maintenance schedules.
- Analyze the impact of CMMS on reducing downtime, enhancing preventive maintenance, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Continuous Improvement Initiatives
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement by leveraging CMMS data for informed decision-making.
- Use CMMS-generated reports and analytics to identify trends, areas for optimization, and opportunities for preventive measures.
- Implement feedback loops with maintenance teams to continuously refine and enhance CMMS usage.
Collaboration between Maintenance and Production Teams
- Facilitate collaboration between maintenance and production teams to align maintenance activities with production schedules.
- Establish regular communication channels between maintenance and production teams to coordinate maintenance tasks during planned downtime.
- Foster a collaborative environment that promotes shared goals and efficient use of resources.
Cybersecurity Measures
- Prioritize cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive maintenance and production data.
- Implement robust cybersecurity protocols, including user authentication, data encryption, and regular security audits.
- Train users on cybersecurity best practices to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.



