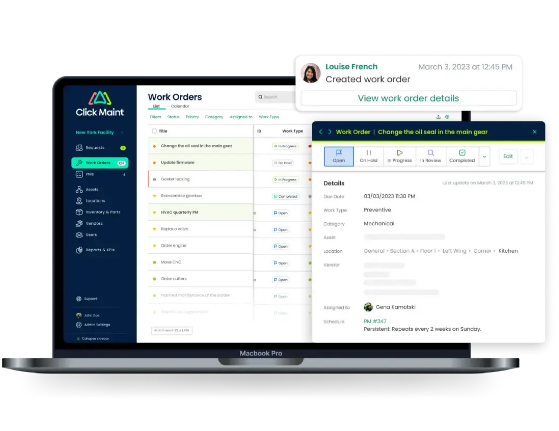
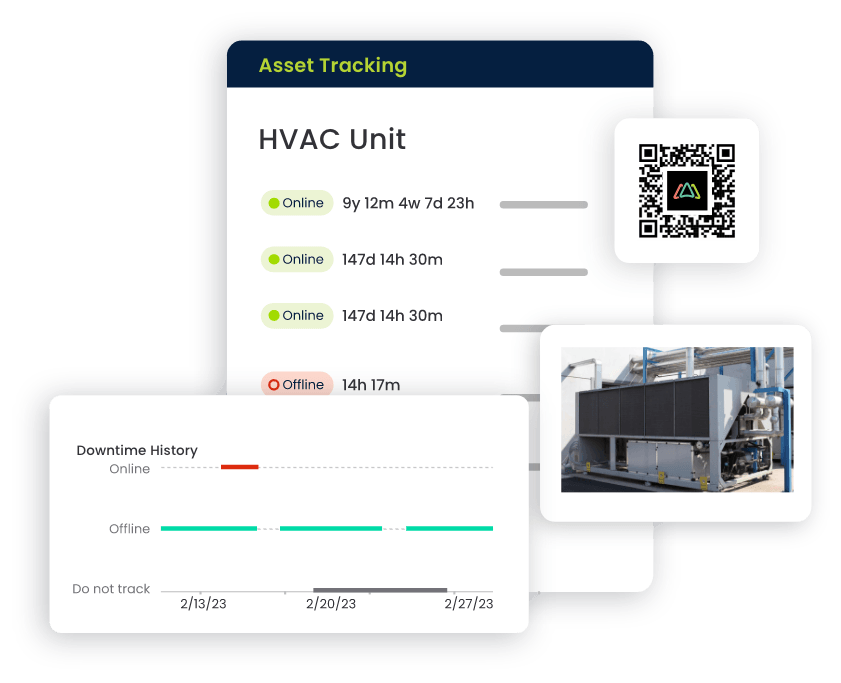
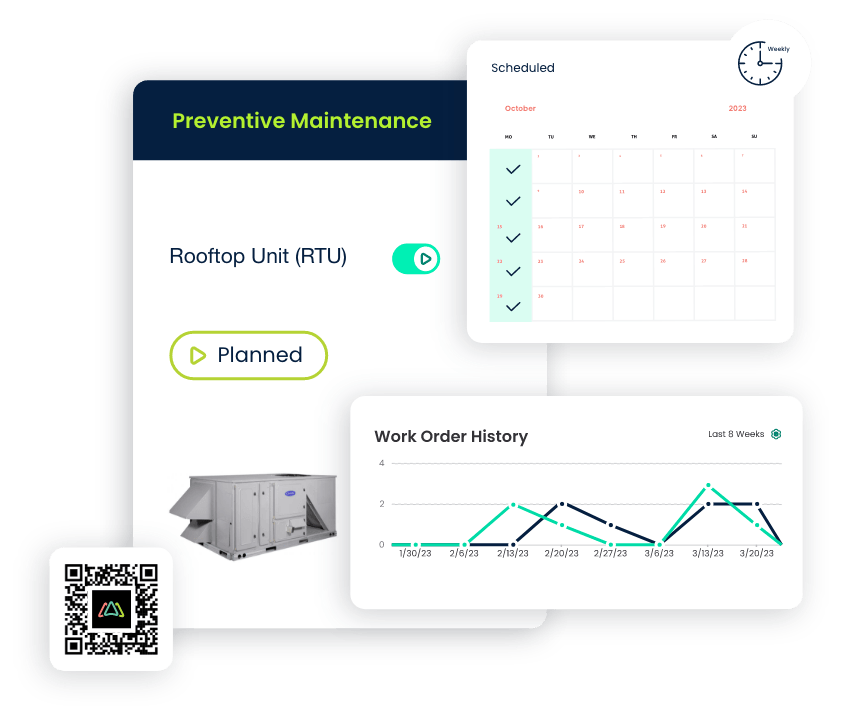
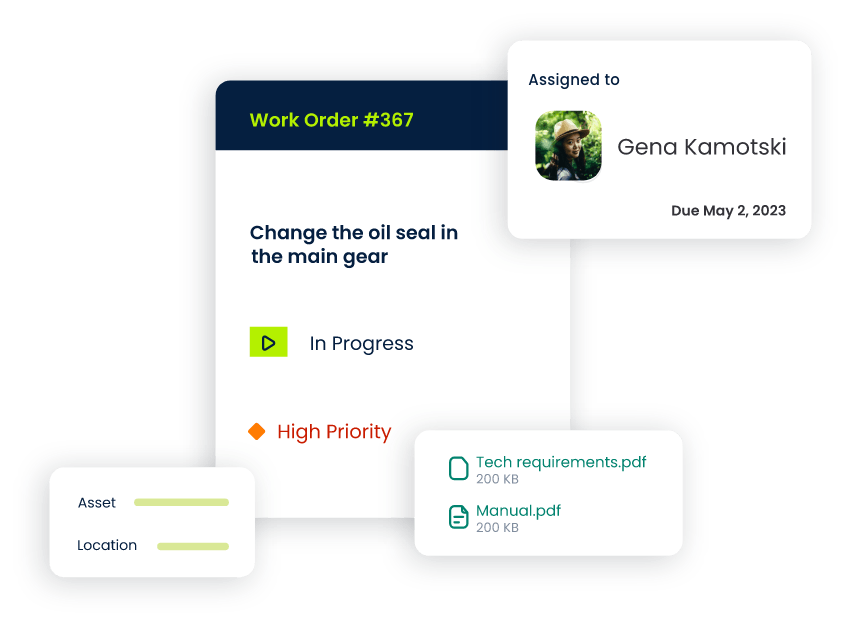
Asset Registration
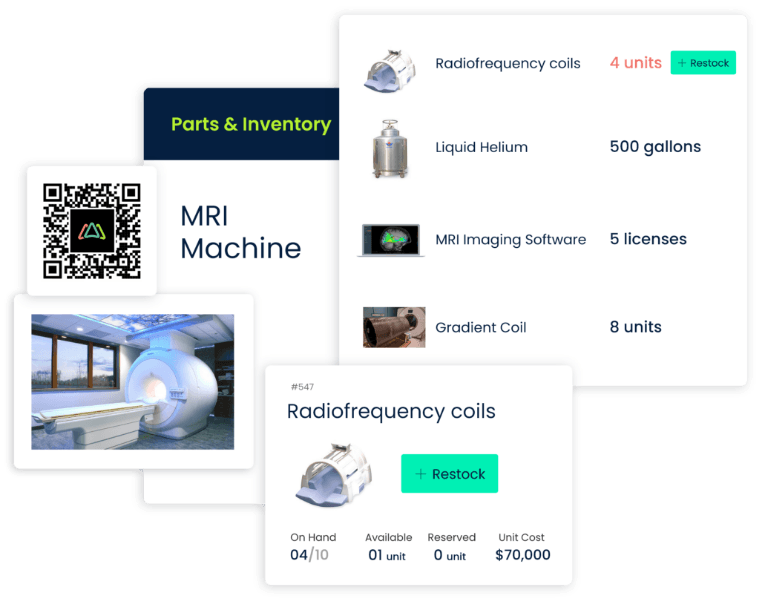
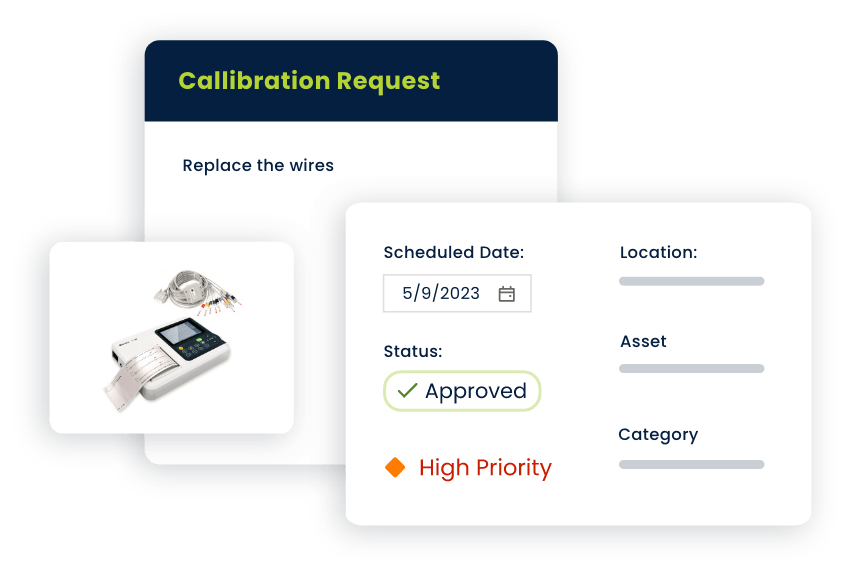
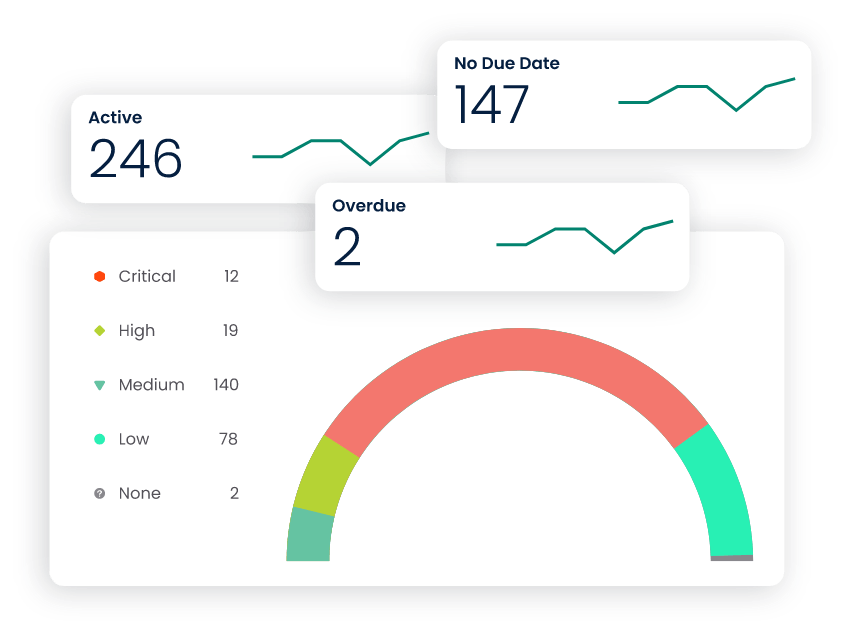
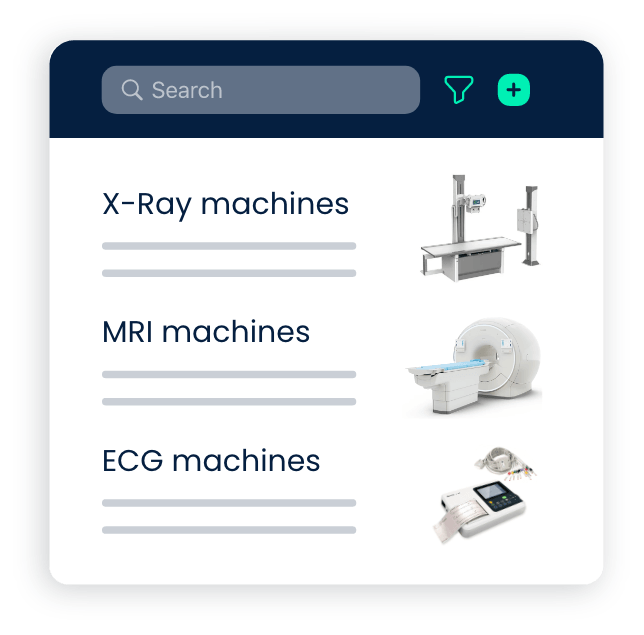
- The process begins with the registration of healthcare assets, including medical equipment, facilities, and infrastructure, into the CMMS database.
- Each asset is given a unique identifier, capturing relevant information such as make, model, serial number, location, supplier, expected life, and maintenance history.