Best CMMS Software for Manufacturing
Streamlining Maintenance Processes for Manufacturing Operations
No credit card required | Start your 30 day FREE trial
- CMMS
- Industry
- CMMS Software for Manufacturing
Labor Efficiency Improvement
Estimated Downtime Reduction
Inventory Optimization
Trusted by thousands of maintenance & facilities professionals





How much does Click Maint CMMS for manufacturing cost?
Try our Price Calculator to get an instant estimate for your maintenance team.
PROFESSIONAL PLAN
$ 42 USD
PER USER PER MONTH
$ 35 USD
PER USER PER MONTH
Manufacturing Maintenance Challenges
Unexpected equipment failures
High unplanned downtime costs
Complex machinery maintenance requirements
Compliance and safety regulations
Inefficient maintenance tracking
High repair and replacement expenses
How CMMS Manufacturing Solves these
Automated work order management
Asset downtime tracking
Maintenance history reporting
Labor and cost tracking
Inventory management and optimization
Automated preventive maintenance scheduling
Click Maint CMMS Manufacturing Features
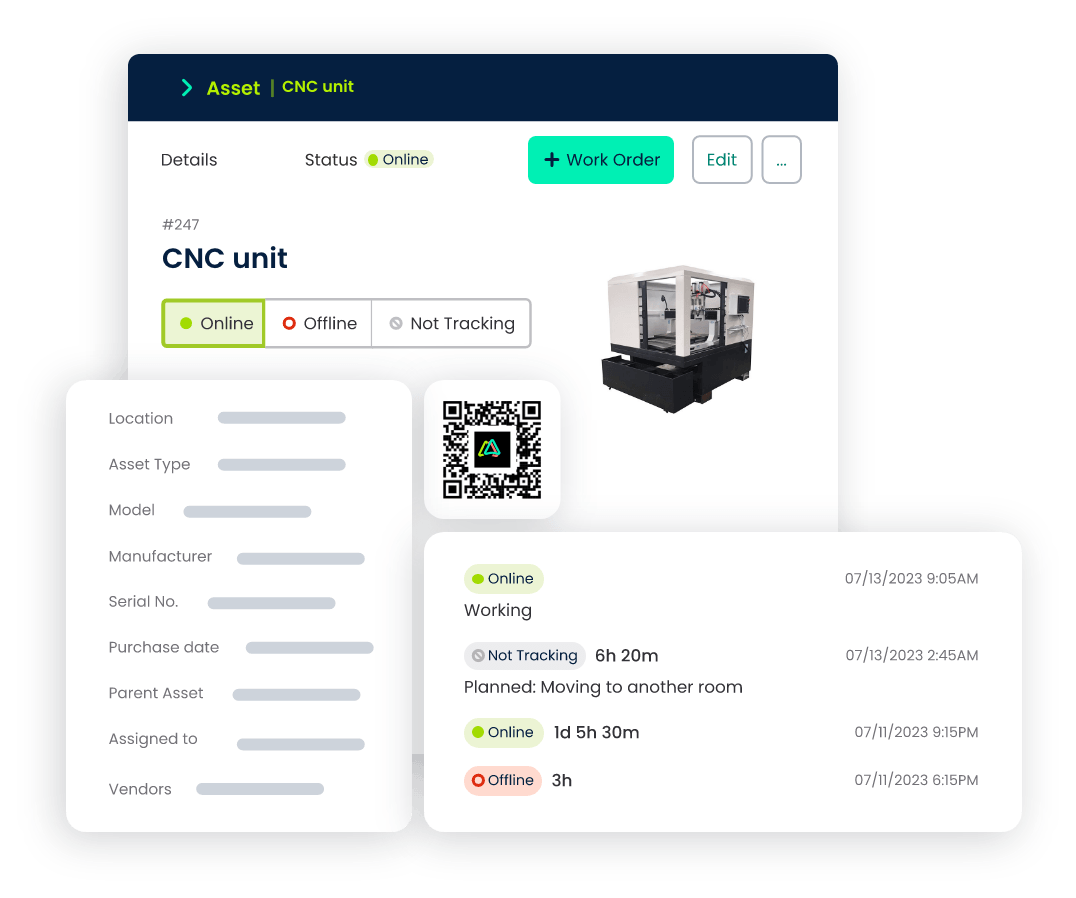
Asset Management
- Track Assets in Real-Time: Monitor the status and performance of manufacturing assets in real time, maintaining an up-to-date inventory of equipment and machinery.
- Schedule Preventive Maintenance: Schedule preventive maintenance tasks based on usage or time intervals, ensuring your assets remain in peak operating condition.
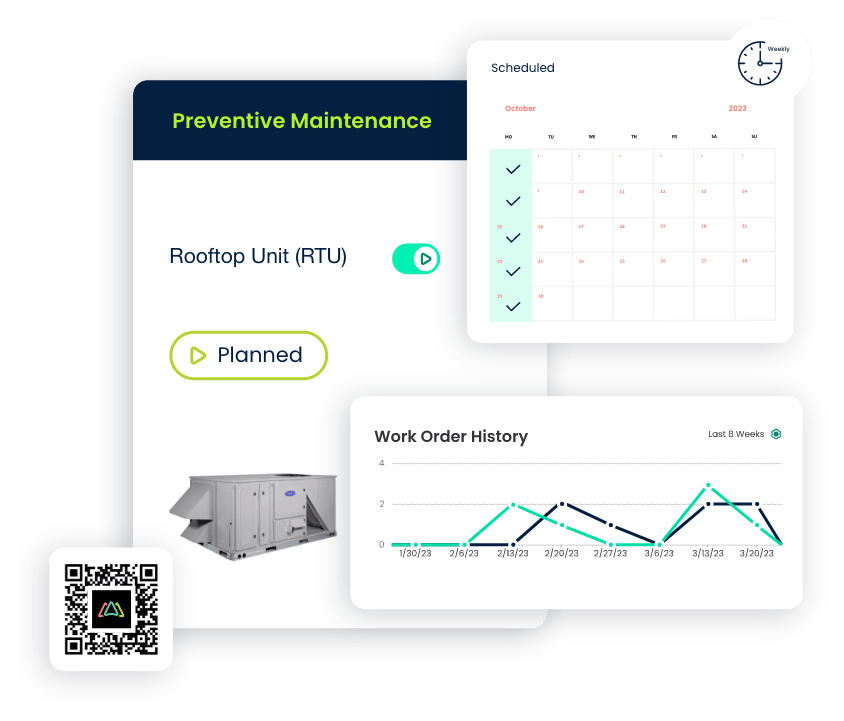
Preventive Maintenance Software for manufacturing
- Automate Maintenance Scheduling: Automate maintenance schedules based on asset usage or predetermined time intervals, ensuring that equipment is regularly inspected and serviced.
- Reduce Unplanned Downtime: Mitigate the risk of equipment breakdowns and costly unplanned downtime through proactive maintenance planning.

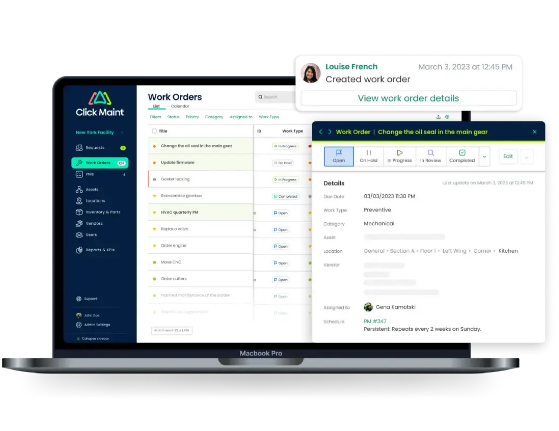
Manufacturing Work Order Software
- Create and Assign Work Orders: Generate and assign work orders, providing detailed instructions and deadlines for maintenance tasks, facilitating a streamlined process.
- Prioritize and Schedule Work Orders: Prioritize tasks and schedule them to align with production timelines, reducing downtime and optimizing operational efficiency.
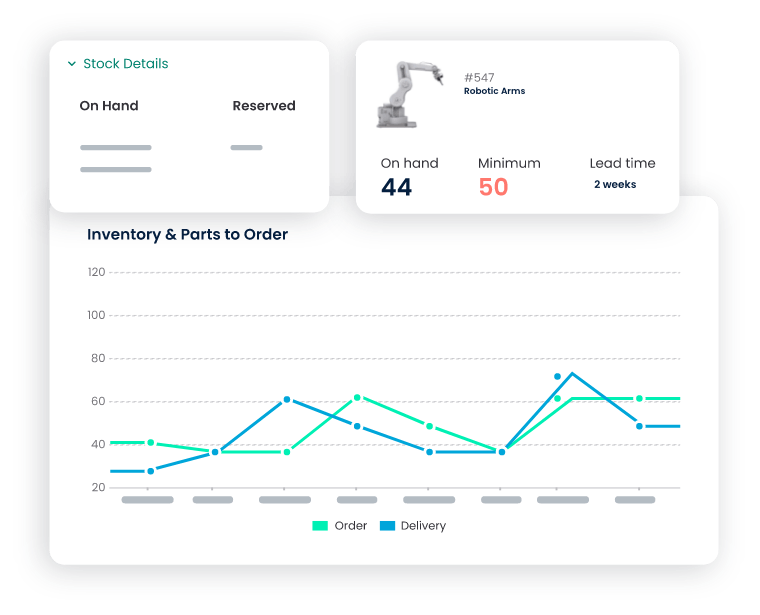
Inventory Management
- Manage Spare Parts: Keep track of spare parts and consumables in inventory, ensuring they are readily available to avoid maintenance delays.
- Optimize Stock Levels: Optimize stock levels by setting minimum and maximum thresholds for inventory items, avoiding overstocking and stockouts.
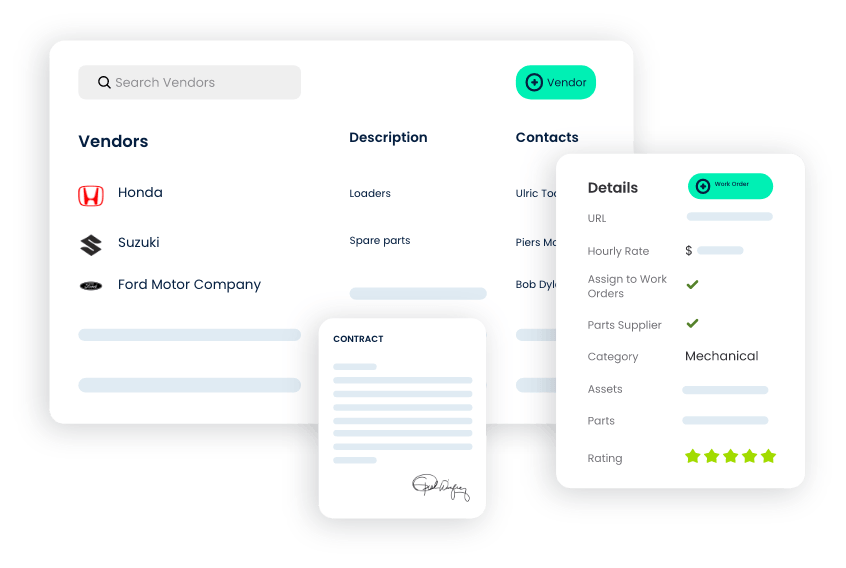
Vendor Management
- Manage Vendor Information: Store and manage essential vendor details, including contact information, service history, and contractual agreements.
- Track Supplier Performance: Monitor vendor performance by assessing metrics like response times, service quality, and adherence to service level agreements.
- Streamline Procurement: Streamline procurement processes by actively notifying the procurement team when parts need to be ordered with details on the required quantity and estimated cost. The system also flags parts that reach their minimum quantity threshold.
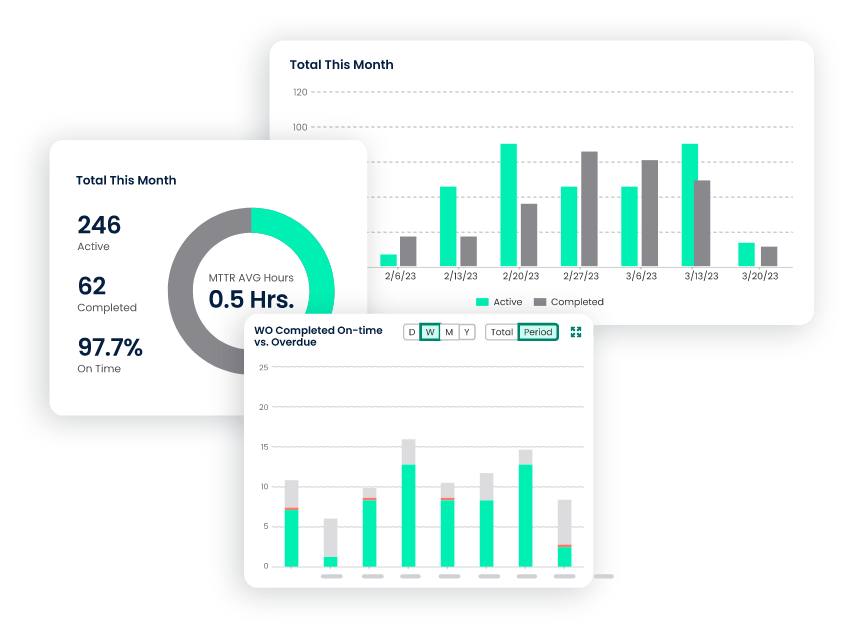
Reporting and Analytics
- Track Performance Metrics: Actively monitor key performance metrics (KPIs) such as mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR), gaining insights for improvement.
- Gain Maintenance Insights: Actively utilize data and analytics to receive maintenance insights. This empowers you to forecast maintenance needs and proactively prevent unplanned downtime.
Experience Click Maint CMMS now
30-Day Free Trial
No Credit Card needed.
Instant access to all features & modules with an optional live walk-through with a Click Maint expert
Book a live Demo
In this 30-minute demo, see firsthand how our easy CMMS can streamline your operations, enhance productivity, and reduce downtime.
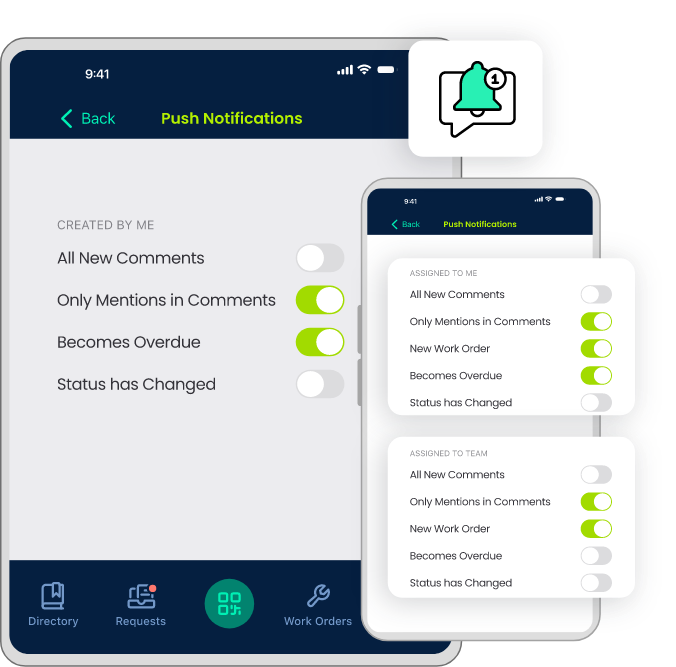
Easy-to-Use Mobile App: Get Work Orders Done on the Go.

Real-Time Data Access
Mobile CMMS apps grant technicians real-time access to important maintenance data. Whether they are on the factory floor, in the field, or even off-site, technicians can check work orders, review asset histories, and access equipment manuals with a few taps on their mobile devices. This real-time access ensures they have up-to-date information to make informed decisions and perform tasks effectively.
Immediate Work Order Updates
Technicians can actively update work orders as they complete tasks. Whether it's noting inspection results, recording repairs, or updating asset information, these updates are instantly synchronized with the central CMMS database. This means that supervisors and colleagues can immediately see the progress of a maintenance task, facilitating better coordination and decision-making.
Enhanced Productivity
Mobile CMMS actively enhances technician productivity. Instead of returning to a central workstation to retrieve work orders or record maintenance data, technicians can do so on the spot. This minimizes downtime, reduces travel time, and allows them to complete more tasks within a given timeframe.
Improved Communication
Mobile CMMS fosters better communication between technicians and the maintenance team. Technicians can actively communicate issues, request additional resources, or provide updates through the app. This real-time communication ensures everyone stays on the same page, reducing miscommunication and minimizing operational disruptions.
Efficient Resource Allocation
With mobile accessibility, technicians can actively manage their resources more efficiently. They can check spare parts availability, request deliveries, and schedule maintenance tasks on-site. This streamlines resource allocation and minimizes delays caused by missing parts or scheduling conflicts.
Enhanced Flexibility
Mobile CMMS actively offers flexibility in task management. Technicians can access the CMMS app on their preferred mobile device, whether a smartphone or tablet. This means they can choose the tools that suit their work style and needs, increasing their comfort and efficiency.
Training and Support
CMMS vendors actively offer training and support for mobile app usage. This helps technicians familiarize themselves with the app's features and functions, ensuring they can actively leverage the mobile platform to its fullest potential.
See how affordable Click Maint CMMS is
Why Conventional Maintenance Approaches Fall Short

Spreadsheets and Paper-Based Systems
Spreadsheets and paper-based systems are manual, time-consuming, and prone to errors. They lack real-time tracking and often lead to inefficiencies, mismanagement of resources, and delays in maintenance tasks. In a manufacturing setting, where precision and speed are critical, these outdated systems are increasingly inadequate.

Lack of Data-Driven Insights
One of the most significant drawbacks of traditional maintenance approaches is the absence of data-driven insights. Without access to historical data and analytics, manufacturers lack the ability to make informed decisions regarding equipment maintenance, upgrades, or process improvements. They operate in the dark, making it challenging to optimize resources and reduce downtime effectively.

Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance is the age-old approach of "fixing it when it breaks." While it may seem cost-effective in the short term, it has significant downsides, particularly in manufacturing. When a critical piece of equipment fails unexpectedly, it can lead to costly downtime, lost production, expensive emergency repairs, and potential safety hazards. Reactive maintenance doesn't align with the unyielding pace and reliability demands of manufacturing.
CMMS Manufacturing Benefits
CMMS provides a structured framework for organizing and optimizing maintenance operations. It is a digital hub consolidating all maintenance-related data, tasks, and documentation. This centralized approach ensures that critical maintenance activities are carried out efficiently, proactively, and with the high degree of precision required in the manufacturing industry.
Equipment Reliability and Uptime
- CMMS systems enable manufacturers to proactively manage and maintain machinery, reducing unexpected breakdowns.
- Preventive maintenance features help track potential issues, preventing costly downtime and disruptions in production.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
- Efficient work order management and scheduling ensure maintenance tasks are carried out at the right time, avoiding conflicts with production schedules.
- CMMS helps prioritize maintenance tasks, reducing idle time and streamlining operations.
Cost Reduction and Better ROI
- By preventing unexpected equipment failures, manufacturers save on costly emergency repairs and replacement parts.
- CMMS assists in optimizing inventory and reducing waste by keeping track of spare parts and consumables.
Compliance and Safety
- CMMS helps manufacturers adhere to industry-specific regulations, ensuring product quality and safety.
- Regular maintenance and documentation support audits, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated fines.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
- CMMS collects and analyzes data, providing valuable insights into equipment performance and maintenance trends.
- These data-driven insights empower manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding upgrades, replacements, and process improvements.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
- Proactive maintenance through CMMS reduces resource consumption, prolonging the lifespan of equipment and reducing waste.
- Manufacturers can align with sustainability goals by minimizing energy usage, emissions, and environmental impact.
Workforce Empowerment
- CMMS enhances collaboration by providing real-time access to work orders and equipment status, enabling seamless communication between maintenance teams and production staff.
- Technicians have access to historical data and maintenance instructions, improving efficiency.
Continuous Improvement
- CMMS software supports a culture of continuous improvement by allowing manufacturers to track key performance indicators and benchmark against industry standards.
- Regularly optimizing maintenance strategies and workflows leads to increased efficiency and cost savings.
Scalability and Adaptability
- CMMS can grow with your manufacturing operations, adapting to the changing needs of your business, whether you're expanding or diversifying your product lines.
Regulatory Compliance and CMMS
Regulatory compliance is a concern in the manufacturing industry that requires strict adherence to industry-specific regulations to ensure product quality, safety, and environmental responsibility. Leveraging a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can significantly aid manufacturing facilities in meeting and maintaining compliance standards.

Industry-specific Regulations (e.g., FDA for Food Manufacturing)
Active Adherence to Regulations
Manufacturing spans various sectors, each with its unique set of regulations. For instance, food manufacturing must comply with stringent regulations established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These regulations encompass food safety, labeling, and record-keeping requirements.
Compliance Complexity
Industry-specific regulations are often complex, frequently changing, and vary by location. Manufacturers are responsible for staying current with these regulations, implementing them, and maintaining meticulous records to prove compliance.

CMMS as a Compliance Tool
Data Integrity and Traceability
CMMS systems are instrumental in ensuring data integrity and traceability, actively helping manufacturers meet regulatory requirements. Detailed records are maintained, which can be readily accessed during inspections to demonstrate compliance.
Preventive Maintenance
CMMS systems actively support preventive maintenance schedules, which are vital for compliance. Regular equipment maintenance, calibration, and quality checks ensure products meet regulatory standards and remain safe for consumption or use.
Asset Management
CMMS allows for the comprehensive management of assets and equipment. This includes maintaining detailed records of equipment specifications, service history, and compliance-related information, such as certification and calibration dates.
Inventory Control
CMMS assists in maintaining control over spare parts and consumables. This ensures that only approved and compliant materials are used in manufacturing processes.
Implementation of CMMS in Manufacturing
1. Pre-Implementation Planning
- Needs Assessment: Assess your organization's specific needs and requirements. What are your maintenance goals, and what problems are you looking to solve? Actively identifying these needs helps tailor the CMMS solution to your manufacturing operation's unique demands.
- Vendor Selection: Consider factors such as vendor reputation, product features, scalability, and the ability to customize the system to your manufacturing processes. Choose a vendor that actively aligns with your goals and can provide adequate support.
2. CMMS Integration with Existing Systems
CMMS should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and other business applications. This active CMMS integration ensures that all your data and processes work harmoniously, reducing data silos and improving overall efficiency.
3. Data Migration and Setup
Migrating historical maintenance data ensures that past maintenance records are preserved and integrated into the new system. Proper setup of the CMMS includes defining equipment hierarchies, maintenance tasks, and workflows to align with your manufacturing processes.
4. Training and Change Management
Educate your staff on how to use the new system effectively. This may require hands-on training sessions, workshops, and the development of user guides. Implement change management strategies to ensure a smooth transition to the CMMS, actively involving your workforce in the process.
5. Post-Implementation Support and Maintenance
Post-implementation support is an ongoing commitment. Your chosen CMMS vendor should actively provide support and maintenance services to address issues, updates, and modifications. Ensure that your CMMS is continually updated and aligned with changing manufacturing needs.

Optimize your maintenance operations with CMMS Software
CMMS Resources
Maintenance Calculators
Designed to enhance efficiency and precision, these tools are your go-to resource for effective maintenance management. Start optimizing today and keep your operations running smoothly!
CMMS Software for Manufacturing
Trends
Industry 4.0 and IoT Integration
Active IoT Integration: Industry 4.0 is driving a significant shift in manufacturing by actively integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) with CMMS. IoT sensors placed on equipment and machinery provide real-time data on performance and condition. CMMS systems actively harness this data to enable predictive maintenance, ensuring equipment reliability and minimizing downtime.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: IoT integration with CMMS enables manufacturers to make data-driven decisions. Real-time insights into equipment performance, energy consumption, and production quality allow for proactive maintenance and process optimization.
AI and Predictive Maintenance
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is actively transforming maintenance strategies. AI algorithms analyze historical data, equipment performance, and other factors to predict when maintenance is required. This approach minimizes reactive maintenance and significantly reduces downtime.
Efficiency Enhancement: AI-powered CMMS actively optimizes maintenance tasks. It prioritizes work orders, schedules preventive maintenance at the most opportune times, and allocates resources more efficiently, leading to significant cost savings.
Challenges
Complexity of Manufacturing Equipment
Manufacturing equipment is engineered for precision and efficiency, boasting intricate components and systems. Whether it's a CNC machine, a conveyor belt, or a robotic arm, the maintenance of these machines requires specialized knowledge and tools. The complex nature of this equipment demands meticulous care, and even a minor malfunction can lead to costly disruptions.
High Production Demands
Manufacturers operate in a world where time is money and production demands are unrelenting. The pressure to keep production lines running around the clock leaves little room for unplanned downtime. Every minute of inactivity equates to potential revenue loss, underscoring the importance of swift, well-organized maintenance practices.
Regulatory Compliance
The manufacturing industry is heavily regulated to ensure safety, quality, and environmental standards. Manufacturers must adhere to a maze of industry-specific regulations, and non-compliance can result in fines, legal issues, and damage to the brand's reputation. The challenge here is to maintain strict adherence to these regulations while optimizing production schedules.
Variation in Maintenance Tasks
Manufacturers often have diverse equipment in their facilities, each with its own maintenance requirements. Maintenance tasks can vary from routine inspections to complex overhauls. Coordinating and managing this variation while ensuring that each piece of equipment receives the necessary attention is a considerable challenge.
Resource Allocation Challenges
Allocating resources effectively is a perpetual challenge in manufacturing. This includes managing skilled maintenance technicians, spare parts inventory, and budgets. Manufacturers must strike a balance between maintaining equipment, minimizing resource costs, and optimizing production. It's a fine line to tread.
What is Factory Maintenance Software?
Factory maintenance software, often synonymous with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) or Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems, is a digital solution designed to streamline and optimize maintenance activities within a manufacturing facility. It serves as a central hub for tracking equipment, scheduling maintenance tasks, managing work orders, and analyzing performance data to enhance operational efficiency.
Key Features of Factory Maintenance Software
Asset Management
- Inventory Tracking: Monitor all equipment, tools, and parts within the facility.
- Lifecycle Management: Track the lifespan and performance history of assets.
- Documentation Storage: Keep manuals, warranties, and service records centralized.
Work Order Management
- Scheduling Tasks: Assign and prioritize maintenance tasks efficiently.
- Real-Time Updates: Receive status updates on ongoing work orders.
- Resource Allocation: Assign technicians and manage workloads effectively.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
- Automated Alerts: Set up reminders for routine inspections and maintenance.
- Calendar Integration: Visualize maintenance schedules to prevent overlaps.
- Checklists and Protocols: Standardize procedures for consistency.
Inventory Management
- Stock Level Monitoring: Keep track of spare parts and materials.
- Automatic Reordering: Set thresholds for automatic restocking.
- Vendor Management: Manage supplier information and procurement processes.
Reporting and Analytics
- Performance Metrics: Analyze equipment efficiency and downtime.
- Cost Analysis: Track maintenance expenses and identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Custom Reports: Generate reports tailored to specific KPIs and compliance needs.
Integration with IoT and Sensors
- Real-Time Data Collection: Use sensors to monitor equipment conditions.
- Predictive Maintenance: Anticipate failures before they occur using data analytics.
- Remote Monitoring: Oversee operations from anywhere, enhancing responsiveness.
Mobile Accessibility
- On-the-Go Access: Technicians can access work orders and asset information via mobile devices.
- Instant Updates: Real-time communication and data entry from the field.
- Geolocation Features: Locate assets and technicians within the facility.


