- CMMS
- Industry
- CMMS Software for Restaurants
Maintenance Challenges Specific to Restaurants & How CMMS Software Helps
While the restaurant industry is known for its delectable cuisines and inviting atmospheres, behind the scenes, it faces unique maintenance challenges that can significantly impact daily operations. From bustling kitchens to customer-centric dining areas, restaurants grapple with distinct issues that require strategic solutions. The implementation of CMMS in the food service industry brings about a multitude of benefits, ranging from cost savings and enhanced efficiency to improved compliance and minimized downtime. These advantages collectively contribute to the seamless functioning of food service establishments, ensuring they operate at peak performance while maintaining the highest standards of quality and safety.

1. Variable Kitchen Equipment
Challenge
Maintaining optimal temperatures for food storage and a comfortable dining environment is essential. Refrigeration units and HVAC systems are prone to breakdowns, putting food safety and customer comfort at risk
Solution
CMMS aids in scheduling routine maintenance for these systems, including coil cleaning and refrigerant checks. Regular monitoring and preventive maintenance help prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensures compliance with food safety regulations.

2. Refrigeration and HVAC Systems
Challenge
Industrial-grade kitchen equipment, such as ovens, fryers, and grills, undergo continuous heavy usage, leading to wear and tear.
Solution
Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule using a CMMS helps extend the lifespan of equipment. Regular inspections and timely repairs can mitigate the impact of wear and tear from high usage.

3. Grease Buildup in Exhaust Systems
Challenge
Commercial kitchens generate significant grease buildup in exhaust systems, posing fire hazards and impacting ventilation.
Solution
Scheduled and thorough cleaning routines can be managed through CMMS, reducing the risk of fire and ensuring a safe working environment.

4. Plumbing and Drainage Issues
Challenge
Restaurants face frequent plumbing challenges, including clogged drains and malfunctioning faucets, which can disrupt kitchen operations and compromise hygiene.
Solution
CMMS enables the creation of work orders for plumbing issues, ensuring timely repairs and preventing disruptions to kitchen and dining services.

5. Point of Sale (POS) Systems
Challenge
Restaurants depend on POS systems for order processing, billing, and inventory management. Technical glitches and software issues can result in service disruptions.
Solution
Regular software updates and proactive maintenance of POS hardware can be scheduled using CMMS, reducing the risk of system failures during peak hours.

6. Flooring and Furniture Maintenance
Challenge
High foot traffic in dining areas leads to wear and tear on flooring and furniture. Spills and stains are common challenges that require swift attention.
Solution
CMMS can manage work orders and recurring tasks for routine inspections and repairs of flooring and furniture, ensuring a clean and inviting atmosphere for customers.

7. Pest Control
Challenge
Restaurants are susceptible to pest infestations, which can be detrimental to food safety and the overall dining experience.
Solution
Implementing a pest control schedule within CMMS ensures regular inspections and preventive measures are in place to address pest issues promptly.

8. High Staff Turnover
Challenge
The food service industry often faces high turnover rates in staff, resulting in frequent onboarding and training requirements. Ensuring that new staff members are adequately trained on maintenance protocols can be challenging.
Solution
Leveraging the training and documentation features of a CMMS to streamline onboarding processes. The system can house instructional materials, maintenance manuals, and training schedules, facilitating a smoother transition for new staff members.

9. Exterior Maintenance
Challenge
The exterior of a restaurant, including signage, parking areas, and outdoor seating, requires regular maintenance to attract customers.
Solution
CMMS can manage scheduled routine inspections and repairs for exterior elements, contributing to a welcoming and well-maintained appearance.

10. Compliance and Safety Regulations
Challenge
The food service industry is subject to stringent compliance and safety regulations to ensure the well-being of customers and employees. Keeping up with evolving regulations and maintaining compliance can be challenging.
Solution
CMMS with features specifically designed for compliance tracking includes scheduling regular inspections, documenting maintenance activities, and generating reports to demonstrate adherence to health and safety standards.
Key Features of Click Maint CMMS Tailored for the Food Service Industry
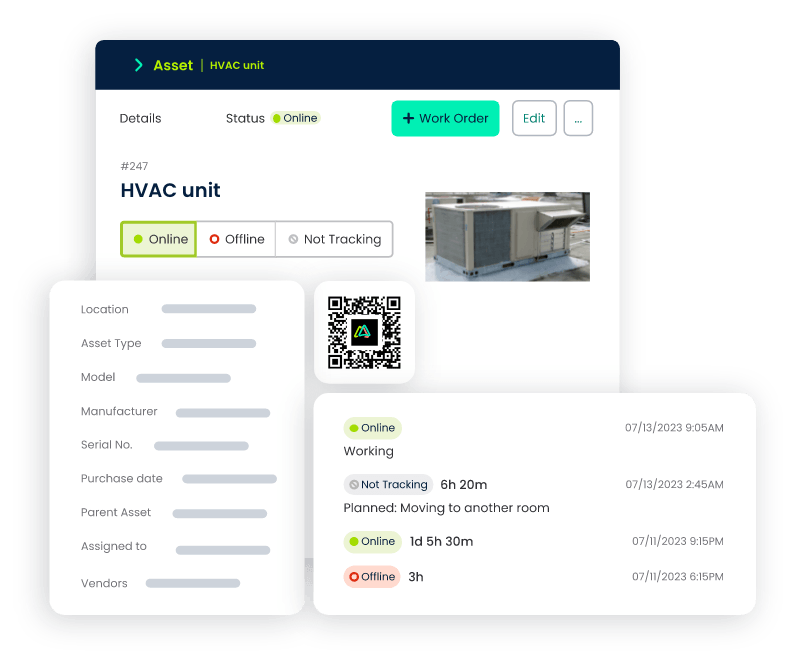
Asset Management
- Importance: Efficient management of kitchen equipment and assets is essential for smooth operations in restaurants and food service establishments.
- CMMS Feature: The robust asset management module centralizes the tracking of all equipment, including ovens, refrigerators, and cooking appliances. It offers real-time insights into asset performance, maintenance history, and lifecycle, empowering decision-makers to make informed choices regarding repair or replacement.
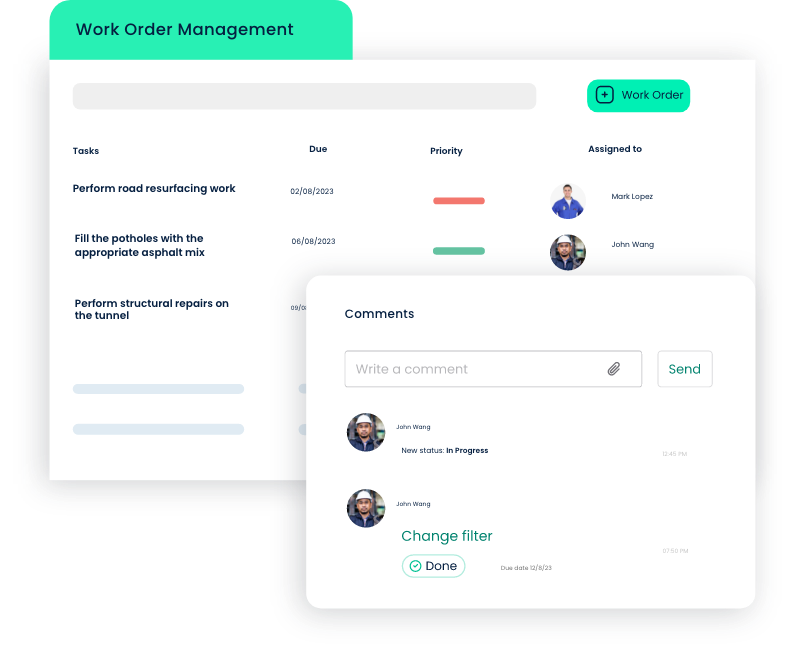
Work Order Management
- Importance: Timely and organized execution of maintenance tasks is critical to prevent disruptions in daily operations.
- CMMS Feature: The work order management feature automates the creation, assignment, and tracking of maintenance tasks. It ensures that all maintenance activities, from routine inspections to urgent repairs, are systematically managed, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. Work orders can be assigned to 3rd party vendors or internal maintenance teams.
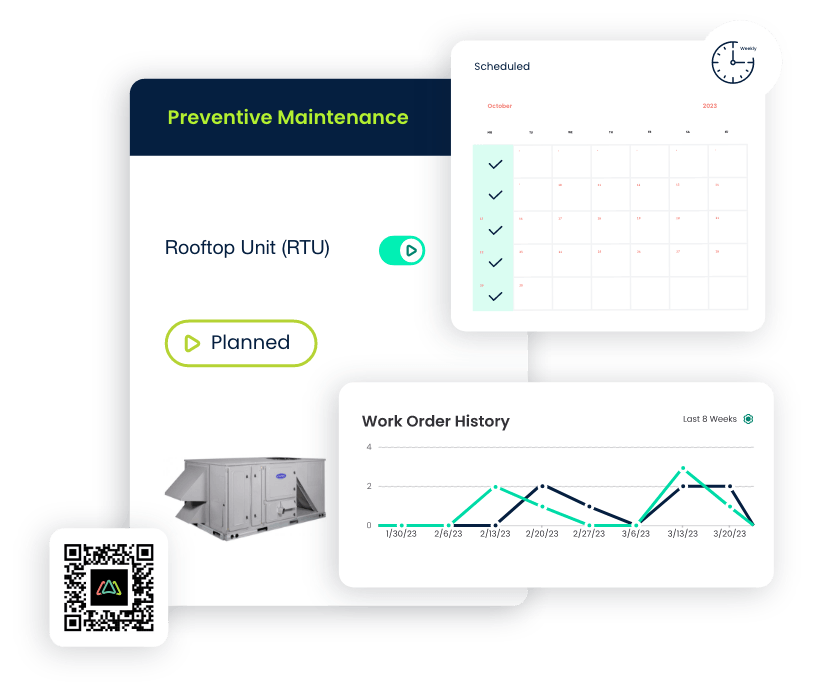
Preventive Maintenance
- Importance: Preventing equipment breakdowns is essential for maintaining a consistent level of service and avoiding unexpected repair costs.
- CMMS Feature: The preventive maintenance module enables the scheduling of routine maintenance tasks based on equipment usage, manufacturer recommendations, or regulatory requirements. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of critical assets. Preventive maintenance tasks can be assigned to 3rd party vendors or internal maintenance teams.
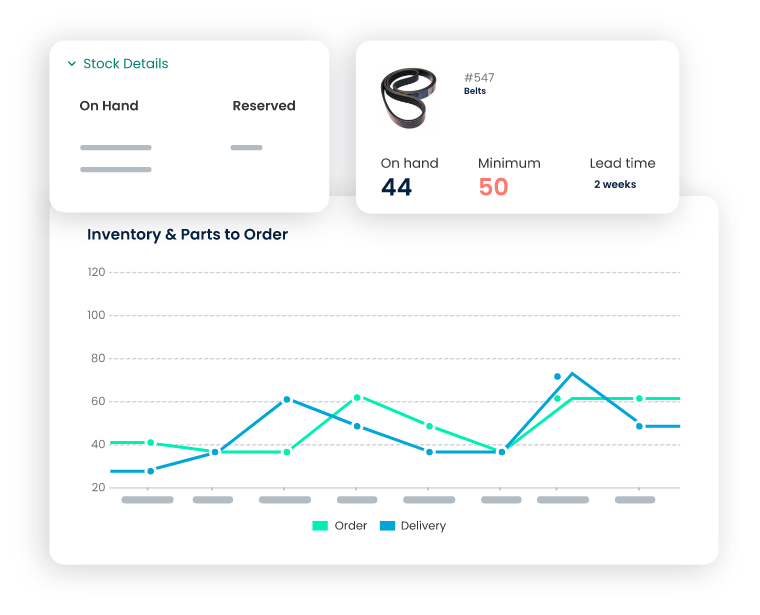
Inventory Management
- Importance: Efficient inventory control is essential for preventing stockouts, minimizing waste, and ensuring the availability of necessary supplies.
- CMMS Feature: Inventory management functionality allows for the optimization of stock levels by providing insights into consumption patterns. It facilitates streamlined procurement processes and prevents overstocking, contributing to cost savings.

Customization for Industry-Specific Needs
- Importance: Every food service establishment has unique operational requirements
- CMMS Feature: Custom fields, workflows, and reporting functionalities ensure that the CMMS aligns seamlessly with the processes and goals of the individual restaurant or food service provider.
Food Safety Compliance Tracking
- Importance: Adherence to food safety regulations is paramount to the success and reputation of any food service establishment.
- CMMS Feature: The system tracks and documents maintenance activities related to food safety, ensuring that equipment meets regulatory standards. It provides a comprehensive audit trail for inspections and repairs, aiding in compliance with health and safety regulations.
Temperature Monitoring and Control
- Importance: For establishments dealing with perishable goods, maintaining optimal temperatures is essential for food safety and quality.
- CMMS Feature: Temperature monitoring capabilities within the CMMS enable real-time tracking and control of refrigeration units and storage areas. Alerts and notifications ensure immediate responses to deviations from set temperature thresholds.

Supplier and Vendor Management
- Importance: Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers and vendors is essential for a reliable and efficient supply chain.
- CMMS Feature: Supplier and vendor management functionalities enable businesses to track supplier performance, manage contracts, and ensure timely deliveries and response to assigned work orders.
Selecting the Right CMMS for Food Service
Assessing Specific Business Needs
Importance:
- Every food service establishment has unique requirements based on its size, scale, and operational nuances. Understanding these specific needs is paramount in selecting a CMMS that aligns seamlessly with the business's objectives.
Considerations:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of maintenance requirements, compliance standards, and operational workflows. Identify key features and functionalities necessary to address the specific challenges of the food service industry.
Vendor Evaluation and Comparison
Importance:
- Choosing a reputable and reliable CMMS vendor is essential for the successful implementation and ongoing support of the system.
Considerations:
- Evaluate potential vendors based on their track record, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Compare features, pricing models, and customer support services to make an informed decision.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Importance:
- As a food service business grows, its maintenance management needs evolve. Selecting a scalable CMMS that can adapt to future requirements prevents the need for frequent system changes.
Considerations:
- Ensure that the chosen CMMS is scalable to accommodate the growth of the business. Evaluate the system's capacity to handle increased asset volumes, additional users, and expanded functionalities.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Solution
Importance:
- The choice between a cloud-based and an on-premises CMMS impacts accessibility, maintenance costs, and system management.
Considerations:
- Assess the advantages and drawbacks of each deployment option. Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility and remote access, while on-premises solutions provide control over data security. Choose the option that aligns with the business's IT infrastructure and preferences.
User-Friendly Interface and Mobile Accessibility
Importance:
- A user-friendly interface and mobile accessibility enhance the usability of the CMMS and support real-time management of maintenance tasks.
Considerations:
- Prioritize CMMS platforms with intuitive interfaces that facilitate easy navigation. Ensure mobile compatibility for on-the-go access, allowing staff to manage work orders and access critical information from anywhere within the facility.
Customer Support and Training
Importance:
- Ongoing support and comprehensive training are vital for the successful implementation and utilization of a CMMS.
Considerations:
- Evaluate the quality of customer support services provided by the vendor. Ensure that adequate training programs are available to equip staff with the knowledge and skills required for effective CMMS utilization. Consider factors such as user documentation, training materials, and access to support resources.
CMMS Implementation for Restaurants
Developing a Comprehensive Implementation Plan
Importance:
- A well-structured implementation plan outlines the entire process, from initial setup to system launch.
Key Steps:
- Define clear objectives, establish a timeline, allocate resources, and designate responsibilities. Consider factors such as data migration, customization, and training requirements.
Data Migration and Integration with Existing Systems
Importance:
- Ensuring seamless data migration and integration with existing systems prevents data discrepancies and promotes consistent information flow.
Considerations:
- Identify data sources and establish a migration plan. Integrate the CMMS with other relevant systems, such as an ERP, accounting software or inventory management systems, to create a cohesive and interconnected operational environment.
Staff Training and Change Management
Importance:
- The successful adoption of a CMMS relies on effective training and change management strategies to engage and empower staff.
Approach:
- Develop a training program tailored to the needs of different user roles. Communicate the benefits of the CMMS and address concerns. Foster a culture of adaptability and continuous improvement to embrace the changes introduced by the new system.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Importance:
- Rigorous testing is essential to identify and rectify any issues before the system goes live. Quality assurance ensures that the CMMS meets performance expectations.
Steps:
- Conduct thorough testing of all functionalities, simulate real-world scenarios, and address any identified issues promptly. Verify data accuracy and system responsiveness to guarantee a smooth user experience.
Go-Live and Post-Implementation Evaluation
Importance:
- The go-live phase marks the official launch of the CMMS into daily operations. Post-implementation evaluation assesses the system's performance and identifies areas for refinement.
Steps:
- Work with your CMMS provider to execute the go-live plan with careful monitoring and support mechanisms in place. Gather feedback from users to identify any post-implementation challenges or improvement opportunities. Conduct a comprehensive evaluation to ensure that the CMMS aligns with business objectives and operational needs.
Best Practices in CMMS Utilization for Restaurants
Once a CMMS is successfully implemented, leveraging it effectively becomes essential for sustained success in the food service industry.
Creating Preventive Maintenance Schedules for Kitchen Equipment
Best Practice:
- Establishing proactive preventive maintenance schedules for kitchen equipment is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Approach:
- Utilize the CMMS to schedule routine inspections, cleaning, and servicing of kitchen appliances. Set automated reminders for preventive maintenance tasks based on equipment usage, manufacturer guidelines, and regulatory requirements.
Efficient Work Order Management for Repairs and Maintenance
Best Practice:
- Streamlining work order management processes contributes to faster response times and minimized downtime for critical equipment.
Approach:
- Leverage the CMMS to automate the creation, assignment, and tracking of work orders. Prioritize tasks based on urgency and allocate resources efficiently. Use the system to communicate updates and resolutions to all relevant stakeholders.
Real-time Monitoring of Critical Parameters (Temperature, Humidity, etc.)
Best Practice:
- Real-time monitoring of critical parameters, such as temperature and humidity, is essential for food safety and regulatory compliance.
Approach:
- Implement sensors and monitoring devices connected to the CMMS for continuous tracking of environmental conditions. Set up alerts and notifications to prompt immediate action in case of deviations from predefined thresholds.
Inventory Optimization and Supplier Relationship Management
Best Practice:
- Optimizing inventory levels and managing supplier relationships contribute to cost savings and operational efficiency.
Approach:
- Utilize the CMMS to analyze consumption patterns, forecast demand, and optimize stock levels. Implement features that facilitate effective communication with suppliers, track performance, and ensure timely deliveries.
Compliance Tracking and Reporting
Best Practice:
- Continuous compliance tracking and reporting are essential to meet regulatory standards and demonstrate adherence to industry norms.
Approach:
- Build compliance tracking reports in the CMMS to document maintenance activities, inspections, and equipment certifications. Generate comprehensive reports for regulatory audits and internal assessments.

