Asset Lifecycle Management: From Acquisition to Disposal
One crucial aspect that can make or break a company's success is the effective management of its assets or equipment throughout their lifecycle. In today's hyperconnected world, where technological advancements are revolutionizing industries at an unprecedented pace, organizations can no longer afford to overlook the strategic potential of managing an equipment’s life cycle.
According to Deloitte, organizations that effectively implement asset lifecycle management have the potential to reduce operational expenditure (OPEX) by up to 15% and capital expenditure (CAPEX) by up to 8% by accurately determining the optimal time to replace assets.
For organizations from manufacturing giants seeking to optimize their production lines, service-based companies aiming to enhance their customer experience, to government entities or municipalities striving for efficient infrastructure management, Asset Lifecycle Management can be the catalyst that propels them to new heights.
What is Asset Lifecycle Management?
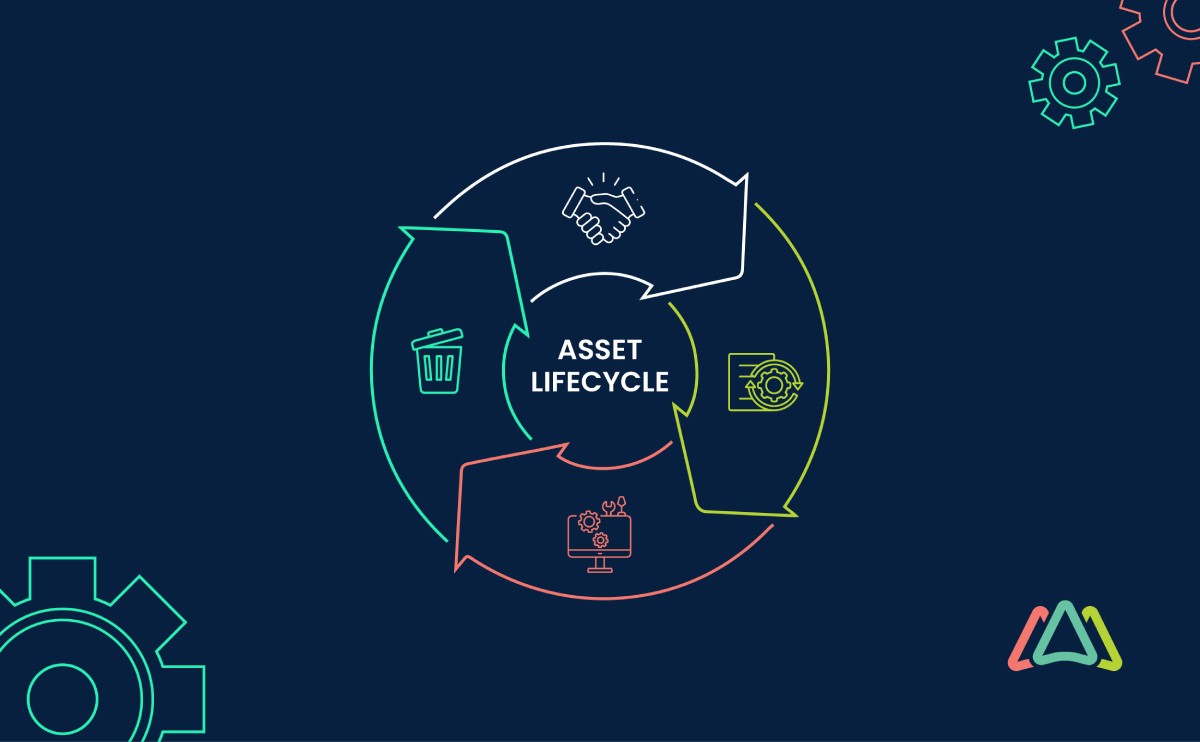
Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a strategic approach in asset management. It encompasses the life journey of an asset - from procurement to disposal. Key stages of ALM include meticulous planning, strategic acquisition, efficient utilization, diligent maintenance, and ultimately, the careful disposal of assets. The fundamental objective of ALM is not merely to extend the useful life of assets, but also to enhance productivity while minimizing associated costs. In essence, asset lifecycle management plays a crucial role in optimizing business resources while contributing to overall profitability.
The Need for Asset Lifecycle Management
Effective asset lifecycle management is crucial for businesses of all sizes and across various industries. Here are some key reasons why ALM is important:
Cost Optimization
ALM helps businesses optimize costs associated with asset acquisition, maintenance, and disposal. By strategically managing assets, businesses can avoid unnecessary purchases, reduce maintenance expenses, extend equipment lifespan, and maximize return on investment.
Improved Asset Utilization
ALM ensures that assets are utilized efficiently throughout their lifespan. By tracking asset usage, monitoring performance, and optimizing allocation, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and increase operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance for Asset Management
Many industries have specific regulations and compliance requirements regarding asset management, maintenance, and disposal. ALM helps businesses ensure they meet these regulatory obligations, avoid penalties, and maintain a good reputation.
Enhanced Decision-making
Effective Asset Lifecycle Management provides organizations with accurate and real-time data on asset performance, maintenance history, and associated costs. These data enable informed decision-making regarding asset replacement, upgrades, and budget allocation.
Key Stages of Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset lifecycle management (ALM) consists of a series of stages that span from the initial acquisition and procurement of assets to their eventual retirement and disposal. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring assets are utilized efficiently, maintained properly, and retired responsibly.
Asset Acquisition and Procurement
Asset acquisition and procurement involve acquiring new assets to meet the needs of a business. This stage is crucial for setting the foundation for effective asset lifecycle management. Here are the key steps to follow:
Define asset requirements
Clearly define the specific requirements and specifications of the assets needed. Consider factors such as capacity, functionality, compatibility, and budget constraints.
Research and select suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers who can provide the required assets. Assess their reliability, quality of products, pricing, delivery capabilities, and customer support.
Negotiate contracts and agreements
Engage in negotiations with the selected suppliers to establish mutually beneficial contracts and agreements. Discuss terms and conditions, warranties, service-level agreements, and pricing.
Procure and receive assets
Once the contracts are finalized, the procurement process begins. Place orders, coordinate delivery logistics, inspect received assets for quality and quantity, and ensure proper documentation of the procurement transactions.
Asset Deployment and Utilization
The asset deployment and utilization stage focuses on effectively deploying and utilizing acquired assets to optimize productivity and achieve business objectives. Here are the key steps involved:
Asset inventory and tracking
Create a comprehensive inventory of all assets, including relevant details such as asset type, serial numbers, and locations. Utilize asset tracking tools and systems to streamline this process and enable real-time asset visibility.
Asset tagging and labeling
Properly tag and label assets with unique identifiers, such as barcodes or RFID tags to help with accurate identification, tracking, and management. This helps to enable easy asset identification, reduces the chances of loss or misplacement, and streamlines asset audits.
Asset allocation and utilization tracking
Assign assets to specific departments or individuals based on operational needs to ensure optimal asset utilization. Track asset allocation and usage to help identify underutilized assets, minimize redundancy, and make informed decisions regarding reallocation or retirement.
Monitoring asset performance and usage
Regularly monitor asset performance, including factors like maintenance requirements, energy consumption, or production output to identify potential issues or opportunities for improvement. Collect relevant data and conduct performance analysis to facilitate proactive maintenance, and enhance asset efficiency.
Asset Maintenance and Monitoring
Effective asset maintenance and monitoring is crucial for maximizing asset lifespan, minimizing downtime, and ensuring optimal performance. Here are the key steps involved:
Establishing preventive maintenance schedule
Develop and implement regular maintenance schedules based on asset manufacturer recommendations and industry best practices. This includes routine inspections, lubrication, calibration, and replacement of components to prevent breakdowns and optimize asset performance.
Conducting regular inspections and audits
Regular inspections help identify any potential issues or signs of wear and tear. Audits involve comprehensive assessments of asset condition, functionality, safety compliance, and adherence to maintenance protocols.
Implementing condition-based maintenance
Leverage advanced technologies and sensors to monitor asset condition in real-time to allow for condition-based maintenance. This approach involves performing maintenance activities based on the asset's actual condition and performance data, reducing unnecessary maintenance costs.
Tracking maintenance history and costs
Maintain a detailed record of maintenance activities, including repairs, replacements, and associated costs, preferably on a cloud-based CMMS system. This historical data helps track asset performance, identify recurring issues, and make data-driven decisions regarding repairs, upgrades, or asset replacements.
Asset Retirement and Disposal
The asset retirement and disposal stage focuses on properly retiring and disposing of assets that have reached the end of their lifecycle. Here are the key steps involved:
Identify end-of-life assets
Regular asset audits and condition assessments help identify assets that have become obsolete, inefficient, or no longer meet operational requirements. Establish criteria for asset retirement to determine when assets should be retired.
Evaluate disposal options (e.g., sale, recycling)
Assess various disposal options based on environmental impact, potential revenue generation, and compliance requirements. Consider options such as selling assets to third parties, recycling, or donating them to charitable organizations.
Properly dispose of assets
Follow the appropriate processes and procedures for asset disposal. Decommission, remove sensitive data, and ensure compliance with regulations or legal obligations. Proper disposal safeguards against environmental harm and potential data breaches.
Document asset retirement process
Maintain detailed documentation, again on a cloud-based CMMS software, of the asset retirement process for legal and financial purposes. Keep records of asset retirement dates, disposal methods, associated costs, and any necessary legal documentation.
Effectively managing these key stages of asset lifecycle management ensures optimized asset utilization, cost control, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making throughout the entire lifespan of assets.
Best Practices for Effective Asset Lifecycle Management
Implementing effective asset lifecycle management (ALM) practices is essential for businesses to optimize asset performance, minimize costs, and ensure compliance. Here are some best practices for them to consider:
Implement a Centralized Asset Management System
Organizations should implement a centralized asset management system to have a comprehensive view of their assets, streamline processes, and improve efficiency. A robust asset management software solution can facilitate tasks such as asset tracking, maintenance scheduling, and reporting. It provides real-time visibility into asset data, enhances collaboration across departments, and enables informed decision-making.
Conduct Regular Asset Audits and Inventory Checks
Regular asset audits and inventory checks are crucial for maintaining accurate records and identifying discrepancies. By conducting periodic audits, businesses can ensure that their asset data are up to date, identify missing or misplaced assets, and reconcile any discrepancies. This practice helps prevent inventory errors, minimizes asset loss, and improves overall asset management.
Develop Standardized Asset Management Policies and Procedures
Developing standardized asset management policies and procedures promotes consistency and ensures that best practices are followed throughout the organization. Clear guidelines should be established for asset acquisition, deployment, maintenance, retirement, and disposal. Standardizing processes enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and enables seamless collaboration among employees or teams responsible for asset management.
Utilize Asset Tracking Technologies (e.g., RFID, Barcode)
Leverage asset tracking technologies such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcodes to improve asset visibility, accuracy, and traceability. These technologies enable quick and accurate asset identification, tracking, and data capture. By using handheld scanners or mobile devices, businesses can streamline asset audits, reduce manual errors, and enhance asset management efficiency.
Train Employees on Proper Equipment Handling and Maintenance
Properly trained employees play a crucial role in effective asset management. Provide comprehensive training on proper asset handling, maintenance procedures, and safety protocols to ensure that employees are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. Regular training sessions and ongoing refresher courses help employees understand the importance of asset management, improve asset care, and minimize the risk of damage or misuse.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can optimize their asset lifecycle management processes, improve asset utilization, reduce costs, and ensure regulatory compliance. The combination of a centralized asset management system, regular audits, standardized policies, asset tracking technologies, and employee training establishes a strong foundation for efficient and effective asset management throughout the lifecycle.
Challenges and Solutions in Asset Lifecycle Management
Managing the lifecycle of assets comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these challenges is essential for effective asset lifecycle management (ALM). Here are some common challenges businesses face and potential solutions to overcome them:
Lack of Visibility and Control over Assets
Challenge
Businesses often struggle with a lack of visibility and control over their assets. This can lead to inefficiencies, asset misplacement, and difficulty in tracking equipment status and utilization.
Solution
Implement a centralized asset management system to provide real-time visibility into equipment data, location, and usage. Utilize asset tracking technologies, such as RFID or barcode to enable accurate and efficient asset identification and tracking. Regular asset audits and inventory checks help maintain accurate asset records and identify any gaps in visibility.
Gaps in Data Management and Reporting
Challenge
Inefficient data management and reporting can hinder effective asset management. Businesses may face difficulties in collecting, analyzing, and utilizing asset-related data for decision-making and performance evaluation.
Solution
Adopt a data-centric approach with a robust asset management solution, like Click Maint, to help streamline data management and reporting processes. Implement standardized data collection procedures and utilize automated data capture mechanisms to reduce manual errors and improve data accuracy. Generate regular reports and leverage analytics tools to enable businesses to gain valuable insights into asset performance and maintenance.
Address Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Challenge
Compliance with industry regulations and regulatory requirements can pose significant challenges in asset lifecycle management. Failure to comply can result in penalties, legal issues, and damage to reputation.
Solution
Establish clear asset management policies and procedures that are aligned with regulatory requirements. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure ongoing compliance. Train employees on compliance protocols and conduct internal audits to help identify and rectify any compliance gaps. Collaborate with regulatory experts or consultants to get guidance and ensure adherence.
Siloed ALM and Other Business Processes
Challenge
Integrating asset lifecycle management with other business processes, such as procurement, maintenance, and finance, can be complex and challenging. Siloed systems and lack of coordination may lead to inefficiencies and data inconsistencies.
Solution
Encourage cross-functional collaboration and communication to integrate ALM with other business processes. Establish seamless data flow and integration between asset management systems and other enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to ensure data consistency and process alignment. Implement standardized workflows and clearly define responsibilities across departments to facilitate smooth integration and efficient asset management.
By addressing these challenges and implementing the suggested solutions, organizations can overcome hurdles in asset lifecycle management. Improved visibility and control over assets, efficient data management and reporting, compliance adherence, and seamless integration with other business processes enable businesses to maximize the value of their assets, optimize performance, and achieve long-term success.
Trends in Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset lifecycle management (ALM) is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs and demands of businesses. As technology advances and new practices emerge, several trends are shaping the future of ALM. Here are some key trends to watch:
Smart Assets
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing asset management by connecting assets to the digital world. The proliferation of connected and intelligent assets is driven by advancements in technologies such as IoT, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and edge computing. IoT sensors and devices embedded in equipment enable real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics. This integration provides valuable insights into asset performance, health, and usage patterns. Businesses can proactively identify maintenance needs, optimize asset utilization, and improve decision-making based on real-time data.
Adoption of Predictive Maintenance and Artificial Intelligence
Predictive maintenance, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), is gaining traction in ALM. By analyzing historical and real-time asset data, AI algorithms can predict asset failures and recommend maintenance actions. This proactive approach reduces downtime, minimizes unplanned repairs, and maximizes asset uptime. AI-powered CMMS also optimizes maintenance schedules, resource allocation, and inventory management, resulting in cost savings, and improved asset performance.
Cloud-based Asset Management Solutions
Cloud-based asset management solutions have become increasingly popular due to their flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. These solutions centralize asset data storage, enable real-time updates, collaboration across teams and locations, and seamless integration with other enterprise systems. Cloud-based ALM platforms provide a unified view of assets, streamline workflows, and enhance data security. They also support mobile access, empowering field teams to update asset information and perform tasks efficiently.
Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
Sustainability is a growing concern for businesses, and it is influencing ALM practices. There is a shift towards adopting circular economy principles, which emphasize the reuse, recycle, and responsible disposal of assets. Businesses are implementing strategies to extend the asset’s life cycle, refurbish or repurpose assets, and prioritize eco-friendly disposal practices. These initiatives reduce environmental impact, enhance brand reputation, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Data-driven Actionable Insights
ALM is increasingly driven by data analytics and insights. Advanced analytics tools enable businesses to extract valuable information from asset data, such as performance trends, maintenance costs, and asset lifecycle patterns. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making related to asset acquisitions, maintenance strategies, and retirement planning.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
ALM is being integrated with other enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). This integration streamlines processes, enables seamless data flow, and facilitates cross-functional collaboration. Connecting ALM with procurement, finance, and maintenance systems provides a holistic view of assets and supports end-to-end asset management.
As businesses embrace these trends, they can unlock new opportunities for efficient and effective asset management. Embracing asset lifecycle management is a STRATEGIC INVESTMENT for businesses to effectively manage their assets throughout their lifespan, driving long-term success and growth. By adopting ALM best practices, businesses can optimize asset utilization, minimize costs, and achieve operational excellence in today's dynamic and competitive business landscape.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Keep Reading
Ever find yourself checking into a luxury hotel and expecting a relaxing stay, only to find a ...
11 Apr 2025
Organizations are witnessing swift changes in the business environment and confronting a ...
8 Apr 2025
Last month, news outlets and the entire internet was abuzz with the return of NASA astronauts ...
3 Apr 2025
What comes first - CMMS or predictive maintenance? If your answer is either, it is correct. ...
28 Mar 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) talk has become commonplace. Today, engaging in business-focused ...
27 Mar 2025
Imagine a world where machines predict, diagnose, and fix their issues before they fail. This ...
25 Mar 2025
A facility maintenance plan is at the core of a facility’s operations. This organized ...
21 Mar 2025
Think of managing your maintenance operations like managing a championship sports team. Just ...
21 Mar 2025
The maintenance sector is battling a severe talent shortage that threatens to undermine ...
7 Mar 2025
Manufacturing maintenance is the backbone of industrial efficiency, ensuring machines run ...
5 Mar 2025
No one likes playing a guessing game when equipment breaks down. Yet, maintenance teams often ...
4 Mar 2025
The size of the preventive maintenance software market is discussed in millions of dollars, ...
4 Mar 2025
The organizational structure and corporate hierarchy vary from company to company. Large ...
28 Feb 2025
Maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of machinery ...
21 Feb 2025
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical component of corporate social ...
20 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) relies on accurate, well-organized data ...
18 Feb 2025
In an era where technology drives operational efficiency, Computerized Maintenance Management ...
14 Feb 2025
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a key component of modern maintenance ...
13 Feb 2025
Introduction Maintenance management is the foundation of maintenance operations in industries ...
11 Feb 2025
Introduction A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is software designed to help ...
7 Feb 2025





