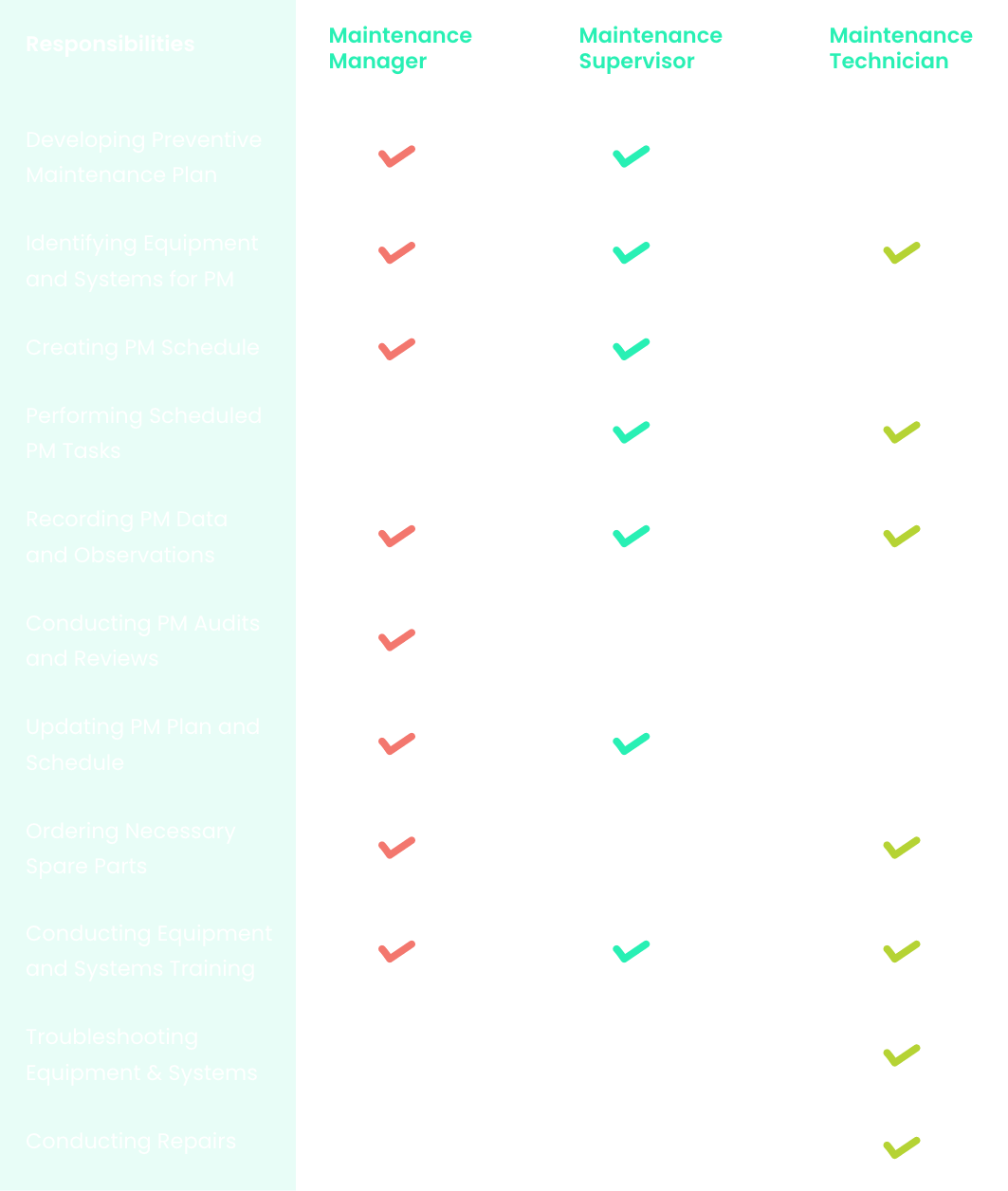
Establish a strong maintenance culture
Maintenance culture matters and because of this creating a healthy maintenance culture is vital.
Essentially, it involves promoting an organizational culture that values maintenance and emphasizes the importance of maintaining equipment. To achieve this, businesses should:
- Emphasize the importance of maintenance to all employees.
- Provide the necessary resources and support for maintenance activities.
- Encourage teamwork and communication between maintenance and other departments.
- Implement a reward and recognition system for maintenance achievements.
- Promote continuous improvement through feedback and employee suggestions.
Utilize metrics and KPIs
Metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are critical in tracking progress and identifying areas for improvement in preventive maintenance programs. Here are some useful metrics and KPIs to consider
1. Equipment uptime and availability
This refers to how long your equipment is up and running, and ready for use. When your equipment is available more often, it means less downtime and increased productivity. When machines are down for hours, production is affected and the potential loss of customers may also be a concern.
Improving equipment uptime and availability is a critical goal of preventive maintenance as it reduces downtime and improves productivity.
2. Mean time between failures (MTBF)
This is a measure of the average time between equipment failures. If an asset is constantly breaking down, considerable time and money will be spent repairing it. On the other hand, a reliable asset that doesn’t require frequent repairs, will operate better and save time and money.
A higher MTBF indicates that equipment is more reliable and requires less maintenance.
3. Mean time to repair (MTTR)
This KPI refers to how long it takes to repair equipment after a failure. The shorter the TTR, the better. That means equipment back up and running faster, which translates to less downtime and more productivity.
4. Planned maintenance percentage (PMP)
Planned Maintenance Percentage measures the percentage of maintenance tasks that are planned and scheduled in advance. A higher PMP is optimal. It translate into being proactive when conducting maintenance tasks, and potentially less likely to experience unplanned downtime.
5. Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Overall Equipment Effectiveness takes into account factors like availability, performance, and quality to measure how efficiently equipment is being used. Improving OEE is a crucial goal of preventive maintenance, as it leads to increased productivity and less downtime.
Tracking and analyzing these KPIs can help business owners make informed decisions and optimize a preventive maintenance program for success. By taking them into account, down time is reduced, productivity is increased, and ultimately time and money is saved.
Regularly review and update the plan
To start, it’s important to remember that preventive maintenance programs are fluid and not static. They should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they stay relevant and effective. Here are some tips to keep in mind
- Conduct regular equipment inspections and condition assessments. This will help identify potential issues before they turn into bigger problems.
- Incorporate feedback from maintenance personnel and other departments. Feedback from team members is important because they can provide valuable insights on what’s working and what’s not. By incorporating their feedback, business owners can improve your program and make everyone’s jobs a little easier.
- Update maintenance procedures based on new equipment or processes. As a business evolves, so will its equipment and processes. Keeping procedures up-to-date will help business owners to stay ahead of any potential issues.
- Stay informed about new technologies and best practices in maintenance. The world is always changing, and there are always new things to learn. By staying informed and incorporating new ideas, business owners can ensure that their program is the best it can be.
Track and analyze data
By keeping a close eye on certain types of data, trends and areas for improvement can be identified, and progress can be tracked. The following are some examples of data to track and analyze:
1. Equipment performance data (e.g., temperature, pressure, vibration, etc.)
Equipment performance data provides valuable insight into the health of equipment.
By keeping abreast on factors such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, problems can be identified before they escalate into something more serious. It provides a warning in advance of an equipment failure. Moreover in doing so, it can save considerable time and money on costly repairs.
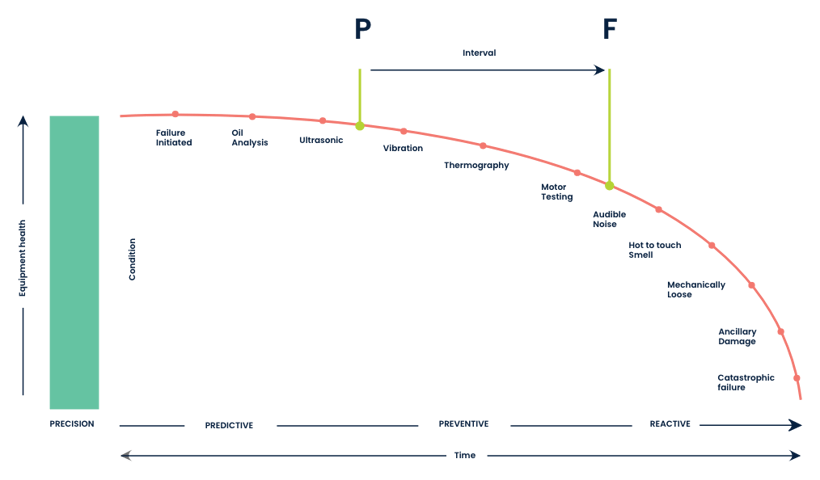
Performance data can be plotted on the PF curve to provide a visual representation of the equipment’s potential failure rate over its remaining useful life (RUL).
By using equipment performance data to build and analyze the PF curve, the following can be identified: early life failure (ELF) period, useful life (UL) period, and wear-out (WO) period of the equipment. This helps maintenance managers plan and schedule preventive maintenance tasks more effectively, by performing maintenance tasks during the UL period to minimize the risk of failure and extend the RUL of the equipment.
2. Maintenance history (e.g., work orders, inspections, repairs, etc.)
This includes information about previous maintenance tasks carried out on the equipment, such as work orders, inspections, repairs, and replacements. By looking at this data, patterns and trends in equipment performance can be identified, which helps in scheduling preventive maintenance tasks more effectively.
3. Downtime data (e.g., cause, duration, frequency, etc.)
This KPI refers to how long it takes to repair equipment after a failure. The shorter the TTR, the better. That means equipment back up and running faster, which translates to less downtime and more productivity.
4. Inventory and spare parts usage
This data includes information about the inventory levels of spare parts and the usage of those parts in maintenance tasks.
By analyzing this data, inventory levels can be optimized, timely availability of spare parts can be ensured, and the downtime caused by unavailability of necessary parts can be decreased.
Tips to design and implement an effective preventive maintenance program
The sooner an effective preventive maintenance program is implemented, the sooner results will be seen. The following are some tips to consider:
- Identify critical equipment and prioritize maintenance tasks accordingly
- Develop detailed maintenance procedures for each piece of equipment
- Use a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) to track and schedule maintenance activities
- Train maintenance personnel on proper maintenance techniques and safety procedures
- Involve all stakeholders in the design and implementation of the program
- Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the program and make adjustments as needed
By following these best practices to design and implementing an effective preventive maintenance program, the lifespan and efficiency of your equipment can be maximized while also minimizing unplanned downtime.